CHAPTER 6 - ELEMENTS OF A STATE
Thursday, 29 April 2021 10:40
INTRODUCTION
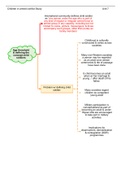
- 5 elements of a state:
i. People
ii. Territory
iii. Authority
iv. Particular government
v. Independence
- All 5 are needed to establish a state
- Different elements are important for constitutional law
i. COMMUNITY OF PEOPLE
- People are necessary for state formation
○ No people = no government =no state
- Government is elected by people to govern people
- Community of people are divided into 2 categories:
○ Citizens
○ Non-citizens (aliens)
a. Citizens
- Citizenship: people with special relationship with a particular country
○ Permanent affiliated/residents of country
○ Have defined rights and responsibilities
○ Afforded Constitutional protection (s 19)
- Citizen vs National
○ Citizen: refers to a relationship between state + individual; local relationship
○ National: used in the international context; indicates country of origin; used in international
relationships
SA citizen is also a SA national
- Section 3: common South African citizenship
- Section 19: allocates political rights
- Section 20: no citizen may be deprived of citizenship
- Section 21: freedom of movement + residence
- Section 22: freedom of trade; occupation and profession
- Section 28: children's rights
a. Non-Citizen (Alien)
- Not a citizen
- Not a permanent affiliation/resident of the country
- Also provided rights and responsibilities; but different
○ Also afforded protection under the C
- E.g. Visitors, foreigners, holiday makers
- In terms of section 19, differentiation/limitations must comply with section 3
- General rule of international law: state may only exercise legislative + executive authority over
citizenship in own country
- Every state has its own rules/system on citizenship
- Each person must have an affiliation with a state or else would be "stateless"
, - Statelessness is regulated into international law and must be prevented
Citizenship and the SA Constitution
- Section 3 (Chapter 1), deals with Citizenship:
○ Cannot be limited (unlike rights in chapter 2, the BoR)
○ Section safeguards common SA citizenship, equal rights, duties + responsibilities
○ Cannot be taken away or limited
Confirmation of common citizenship seen in the case of Kaunda v President of the
Republic of South Africa 2005 (4) SA 235 (CC)
□ SA citizens are entitled to SA government protection in terms of international
law against wrongful acts of a foreign state
○ National law: South African Citizenship Act 88 of 1995
- Section 20: Citizenship
○ no citizen may be deprived of citizenship
○ Right is not absolute
○ Subject to limitation clause (s 36)
○ May limit if reasonable and justifiable
○ Limitations will depend on each individual case + the circumstances thereof
- Section 28: Children
○ Each child has the right from birth to nationality
○ Also seen in international law
Convention of the Rights of the Child
□ Purpose to limit statelessness of children
○ Right is not absolute and may be limited by s36
Unlikely
- Both sections 20+28 are part of the Bill of Rights
- Section 36 (limitation clause) is only applicable to the BoR!
- Constitution in general is supreme (s2)
- Aspects concerning citizenship must comply with Constitution and BoR
○ More details permitted to it ito National Law
- Selected provisions from the SA Citizenship Act 88 of 1995:
○ See pages 175-183
Ways to Acquire/Lose SA Citizenship ito SA Citizenship Act 88 of 1995
- 3 ways to acquire citizenship:
○ Birth
○ Descent
○ Naturalisation
- 3 ways to lose citizenship:
○ Loss
○ Renunciation
○ Deprivation
ii. TERRITORY
- Every state has a demarcated territory
- Territory indicates whether laws are applicable/enforceable
- Ways to demarcate territory:
○ Occupation - vacant/newly discovered land
○ Annexation - acquisition of territory by force
○ Prescription - lengthy + uninterrupted period of occupation
Thursday, 29 April 2021 10:40
INTRODUCTION
- 5 elements of a state:
i. People
ii. Territory
iii. Authority
iv. Particular government
v. Independence
- All 5 are needed to establish a state
- Different elements are important for constitutional law
i. COMMUNITY OF PEOPLE
- People are necessary for state formation
○ No people = no government =no state
- Government is elected by people to govern people
- Community of people are divided into 2 categories:
○ Citizens
○ Non-citizens (aliens)
a. Citizens
- Citizenship: people with special relationship with a particular country
○ Permanent affiliated/residents of country
○ Have defined rights and responsibilities
○ Afforded Constitutional protection (s 19)
- Citizen vs National
○ Citizen: refers to a relationship between state + individual; local relationship
○ National: used in the international context; indicates country of origin; used in international
relationships
SA citizen is also a SA national
- Section 3: common South African citizenship
- Section 19: allocates political rights
- Section 20: no citizen may be deprived of citizenship
- Section 21: freedom of movement + residence
- Section 22: freedom of trade; occupation and profession
- Section 28: children's rights
a. Non-Citizen (Alien)
- Not a citizen
- Not a permanent affiliation/resident of the country
- Also provided rights and responsibilities; but different
○ Also afforded protection under the C
- E.g. Visitors, foreigners, holiday makers
- In terms of section 19, differentiation/limitations must comply with section 3
- General rule of international law: state may only exercise legislative + executive authority over
citizenship in own country
- Every state has its own rules/system on citizenship
- Each person must have an affiliation with a state or else would be "stateless"
, - Statelessness is regulated into international law and must be prevented
Citizenship and the SA Constitution
- Section 3 (Chapter 1), deals with Citizenship:
○ Cannot be limited (unlike rights in chapter 2, the BoR)
○ Section safeguards common SA citizenship, equal rights, duties + responsibilities
○ Cannot be taken away or limited
Confirmation of common citizenship seen in the case of Kaunda v President of the
Republic of South Africa 2005 (4) SA 235 (CC)
□ SA citizens are entitled to SA government protection in terms of international
law against wrongful acts of a foreign state
○ National law: South African Citizenship Act 88 of 1995
- Section 20: Citizenship
○ no citizen may be deprived of citizenship
○ Right is not absolute
○ Subject to limitation clause (s 36)
○ May limit if reasonable and justifiable
○ Limitations will depend on each individual case + the circumstances thereof
- Section 28: Children
○ Each child has the right from birth to nationality
○ Also seen in international law
Convention of the Rights of the Child
□ Purpose to limit statelessness of children
○ Right is not absolute and may be limited by s36
Unlikely
- Both sections 20+28 are part of the Bill of Rights
- Section 36 (limitation clause) is only applicable to the BoR!
- Constitution in general is supreme (s2)
- Aspects concerning citizenship must comply with Constitution and BoR
○ More details permitted to it ito National Law
- Selected provisions from the SA Citizenship Act 88 of 1995:
○ See pages 175-183
Ways to Acquire/Lose SA Citizenship ito SA Citizenship Act 88 of 1995
- 3 ways to acquire citizenship:
○ Birth
○ Descent
○ Naturalisation
- 3 ways to lose citizenship:
○ Loss
○ Renunciation
○ Deprivation
ii. TERRITORY
- Every state has a demarcated territory
- Territory indicates whether laws are applicable/enforceable
- Ways to demarcate territory:
○ Occupation - vacant/newly discovered land
○ Annexation - acquisition of territory by force
○ Prescription - lengthy + uninterrupted period of occupation