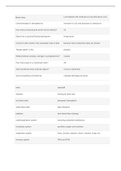
Mitral Valve Lies between left ventricle (LV) and left atrium (LA)
Chemoreceptor is stimulated by increase in CO2 and decrease in arterial pH
How many chromosomes at the end of meiosis? 23
Elbow has a synovial fluid protecting the Hinge joints
Common otitis media in the eustachian tube of kids because their eustachian tubes are shorter
"Master gland" is the pituitary
What produces oocytes, estrogen, & progesterone? ovaries
How many days in a menstrual cycle? 28
what membrane lines external organs? mucous membrane
what is breathing controlled by medulla oblongata and pons
static standstill
dynamic moving at same rate
red blood cells transports hemoglobin
white blood cells fight infections
platelets slow blood flow (clotting)
cardiorespiratory system removing unwanted substances
circulatory system provides oxygen and nutrients
respiratory system nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, etc.
nervous system CNS and PNS
,sympathetic fight or flight
parasympathetic normal condition
neuroendocrine system thalamus and hypothalamus
gastrointestinal system processes nutrients
urinary system kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra, etc.
musculoskeletal system bones, tendons, muscles, joints, ligaments, etc.
3 types of skin epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous
How many bones in skull? 28 (14 facial, 14 cranial)
How many bones in verterbral column? 33
How many phalanges? 56
How many pairs of ribs? 12
Abdominopelvic Cavity composed of the abdomen and pelvis
Absorption Movement of nutrients from the digestive tube to the bloodstream
Actin Protein making up the I Band of the sarcomere
Amino Acid The building block of proteins
Antibody Special proteins that protect the body from foreign substances
ATP Abbreviation for Adenosine triphosphate, which is the energy of the cell. In muscles,
this energy causes filaments to slide together to produce contraction.
Atria Upper chambers of the heart; receives blood
,Blood Consists of approximately 55% plasma and 45% formed elements (erythrocytes,
leukocytes, and platelets). Serves to transport oxygen and nutrients to body cells and
to carry away carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes
Plasma Contains about 10% proteins, ions, nutrients, waste products, and hormones, which
are dissolved or suspended in water.
Formed Element Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets; produced from stem cells in red bone marrow.
Tricuspid Valve Valve on the right side of the heart between the atrium and ventricle
Bicuspid Valve Valve on the left side of the heart between the atrium and ventricle
Semilunar Valve Found at the entrances of the pulmonary trunk and the aorta.
Sinoatrial Node Initiates the heart's intrinsic beat
Electrocardiogram Measurement of the wave of electrical activity within the heart
Systole Contraction phase of the cardiac cycle
Diastole Relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle
Muscle Contraction Results in the sliding together of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle cell or
fiber
Mitosis Necessary for growth and repair. The DNA is duplicated and distributed to 2 daughter
cells.
Meiosis Special cell division that takes place in the gonads. Chromosome number is reduced
from 46 to 23 so wen the egg and the sperm unite in fertilization the zygote will have
the correct number of chromosomes.
Skin The largest organ in the body. Consists of the epidermis and the dermis.
Epidermis Outer, most protective layer of dead keratinized epithelial cells. Contain Melanin.
Stratum corneum - stratum lucidum - stratum granulosum - stratum germinativum
(outer layer to inner).
Dermis Underlying layer composed of fibrous connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve
, endings, and the associated skin structures (hair follicles/glands)
Melanin Protein pigment that protects against radiation from the sun
Eccrine Gland Most widely distributed sweat glands that regulate body temperature by releasing a
watery secretion that evaporates from the surface of the skin
Apocrine Gland Sweat gland that produce a secretion containing cytoplasm. Mainly found in the armpit
and groin areas.
Sebaceous Gland Release an oily secretion through the hair follicles that lubricates the skin and
prevents drying. These glands are susceptible to becoming clogged and attracting
bacteria, particularly during adolescence.
Holocrine Secretion Produces oil; whole cells of the sebaceous gland are part of this secretion
Skeletal System Functions to support, permit movement, form blood cells (homeopoiesis), protect
internal organs, detoxify, point for muscle attachment, mineral storage (particularly
phosphorous and calcium)
Long Bone Has an irregular epiphysis at each end, composed mainly of spongy (cancellous)
bone. Has a shaft (diaphysis) composed of compact bone.
Osteoblast Form compact bone; Once becoming fixed into the bone matrix, they stop dividing but
continue to maintain bone tissue as osteocytes
Diaphysis The shaft composed of compact bone
Epiphysis End of each bone
Axial Skeleton Composed of 28 bones of the skull (14 facial bones and 14 bones of the cranium) and
33 bones of the vertebral column (7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar
vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae, and the coccygeal vertebrae) and the bones of the
thorx, the sternum and the 12 pairs of ribs
Appendicular Includes the girdles and the limbs. Upper pectoral girdle, the clavicle and the scapula,
Skeleton and the upper extremity, and the bones are the arm and hand. Pelvic Girdle or os
coxae, leg, and foot bones.
Actin Causes muscle contraction by sliding together with myosin filaments.
Chemoreceptor is stimulated by increase in CO2 and decrease in arterial pH
How many chromosomes at the end of meiosis? 23
Elbow has a synovial fluid protecting the Hinge joints
Common otitis media in the eustachian tube of kids because their eustachian tubes are shorter
"Master gland" is the pituitary
What produces oocytes, estrogen, & progesterone? ovaries
How many days in a menstrual cycle? 28
what membrane lines external organs? mucous membrane
what is breathing controlled by medulla oblongata and pons
static standstill
dynamic moving at same rate
red blood cells transports hemoglobin
white blood cells fight infections
platelets slow blood flow (clotting)
cardiorespiratory system removing unwanted substances
circulatory system provides oxygen and nutrients
respiratory system nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, etc.
nervous system CNS and PNS
,sympathetic fight or flight
parasympathetic normal condition
neuroendocrine system thalamus and hypothalamus
gastrointestinal system processes nutrients
urinary system kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra, etc.
musculoskeletal system bones, tendons, muscles, joints, ligaments, etc.
3 types of skin epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous
How many bones in skull? 28 (14 facial, 14 cranial)
How many bones in verterbral column? 33
How many phalanges? 56
How many pairs of ribs? 12
Abdominopelvic Cavity composed of the abdomen and pelvis
Absorption Movement of nutrients from the digestive tube to the bloodstream
Actin Protein making up the I Band of the sarcomere
Amino Acid The building block of proteins
Antibody Special proteins that protect the body from foreign substances
ATP Abbreviation for Adenosine triphosphate, which is the energy of the cell. In muscles,
this energy causes filaments to slide together to produce contraction.
Atria Upper chambers of the heart; receives blood
,Blood Consists of approximately 55% plasma and 45% formed elements (erythrocytes,
leukocytes, and platelets). Serves to transport oxygen and nutrients to body cells and
to carry away carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes
Plasma Contains about 10% proteins, ions, nutrients, waste products, and hormones, which
are dissolved or suspended in water.
Formed Element Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets; produced from stem cells in red bone marrow.
Tricuspid Valve Valve on the right side of the heart between the atrium and ventricle
Bicuspid Valve Valve on the left side of the heart between the atrium and ventricle
Semilunar Valve Found at the entrances of the pulmonary trunk and the aorta.
Sinoatrial Node Initiates the heart's intrinsic beat
Electrocardiogram Measurement of the wave of electrical activity within the heart
Systole Contraction phase of the cardiac cycle
Diastole Relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle
Muscle Contraction Results in the sliding together of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle cell or
fiber
Mitosis Necessary for growth and repair. The DNA is duplicated and distributed to 2 daughter
cells.
Meiosis Special cell division that takes place in the gonads. Chromosome number is reduced
from 46 to 23 so wen the egg and the sperm unite in fertilization the zygote will have
the correct number of chromosomes.
Skin The largest organ in the body. Consists of the epidermis and the dermis.
Epidermis Outer, most protective layer of dead keratinized epithelial cells. Contain Melanin.
Stratum corneum - stratum lucidum - stratum granulosum - stratum germinativum
(outer layer to inner).
Dermis Underlying layer composed of fibrous connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve
, endings, and the associated skin structures (hair follicles/glands)
Melanin Protein pigment that protects against radiation from the sun
Eccrine Gland Most widely distributed sweat glands that regulate body temperature by releasing a
watery secretion that evaporates from the surface of the skin
Apocrine Gland Sweat gland that produce a secretion containing cytoplasm. Mainly found in the armpit
and groin areas.
Sebaceous Gland Release an oily secretion through the hair follicles that lubricates the skin and
prevents drying. These glands are susceptible to becoming clogged and attracting
bacteria, particularly during adolescence.
Holocrine Secretion Produces oil; whole cells of the sebaceous gland are part of this secretion
Skeletal System Functions to support, permit movement, form blood cells (homeopoiesis), protect
internal organs, detoxify, point for muscle attachment, mineral storage (particularly
phosphorous and calcium)
Long Bone Has an irregular epiphysis at each end, composed mainly of spongy (cancellous)
bone. Has a shaft (diaphysis) composed of compact bone.
Osteoblast Form compact bone; Once becoming fixed into the bone matrix, they stop dividing but
continue to maintain bone tissue as osteocytes
Diaphysis The shaft composed of compact bone
Epiphysis End of each bone
Axial Skeleton Composed of 28 bones of the skull (14 facial bones and 14 bones of the cranium) and
33 bones of the vertebral column (7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar
vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae, and the coccygeal vertebrae) and the bones of the
thorx, the sternum and the 12 pairs of ribs
Appendicular Includes the girdles and the limbs. Upper pectoral girdle, the clavicle and the scapula,
Skeleton and the upper extremity, and the bones are the arm and hand. Pelvic Girdle or os
coxae, leg, and foot bones.
Actin Causes muscle contraction by sliding together with myosin filaments.