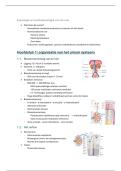
Fysiologie en pathofysiologie van de nier
Ø Wat doen de nieren?
- Verwijderen metabole producten en toxines uit het bloed
- Homeostatische rol:
Volume-status
Elektrolytenbalans
Zuur-base
- Endocrien: erythrogenese, calcium metabolisme, bloeddruk en bloed flow
Hoofdstuk 1: organisatie van het urinair systeem
1.1. Bloedvoorziening van de nier
Ø Ligging: 12e rib tot 3e lumbale wervel
Ø Gewicht: ± 150 gram
- 0,5% van totale lichaamsgewicht
Ø Bloedvoorziening is hoog!
- 20% van de cardiac output = 1L/min
Ø Einddoel: nefronen
- 800 000 – 1 200 000 per nier
85% oppervlakkige nefronen (cortex)
15% juxta-medullaire nefronen (medulla)
(ó morfologie: andere verdeling nefronen)
- Hoge bloedflow nodig om ultrafiltraat (primair urine) te maken
Ø Bloedvoorziening:
- A renalis – a interlobaris – a arcuata – a interlobularis
- aWerente arteriolen
- Glomerulaire kluwen
- Eferente arteriolen
Peritubulaire capillairen (opp nefronen) - v interlobularis
Vasa recta (juxta-medullaire nefronen)
- Vena arcuata – vena interlobaris – vena renalis
1.2. Het nefron
Ø Glomerulus
- Glomerulaire capillairen
- Mesangium (intra- em extraglomerulair)
- Ruimte em kapsel van Bowman
Ø Tubuli
- Proximale tubulus
,- Lis van Henle
è Oppervlakkige nefronen: kort (tot buitenste deel medulla, bijna geen
stijgend deel)
è Juxtamedullaire nefronen: lang
- Distale tubuli
- Connectie (connecting tubule)
- Verzamelbuisjes: lopen teug helemaal door de medulla tot aan de papil
1.2.1. Fysiologie verschillende delen van het nefron
ð Glomerulus vormt een ultrafiltraat van het plasma (primair urine)
- Samenstelling afhankelijk van de ultrafiltratie coëWiciënt en starling
forces
ð Tubulus bewerkt deze primaire urine
ð Proximale tubulus
- Reabsorptie van water en opgeloste stoWen: NaCl, NaHCO3, glucose,
aminozuren, Ca2+, HPO42, SO42_
- Zuur-base: reabsorptie van HCO3-, secretie NH4+
- Secretie organische anionen en kationen
ð Lus van Henle
- Reabsorptie van NaCl
- Opbouw hypertoniciteit in medulla è nodig voor concentreren
(dilueren) van urine
- Secretie van Tamm-Horsfall glycoproteïne (30-50 mg/dl)
è functie nog onduidelijk: waarschijnljk bescherming tubuli
Kunnen soort cilinder vormen: bloedcellen in cilinder bij patiënten
duidt op een probleem in de lus van Henle
ð Distale tubulus en verzamelbuisjes
- Fine tuning van zout en water excretie afhankelijk van status van het
lichaam
- Wateropname of -secretie op basis van de medullaire hypertoniciteit
opgebouwd in de lus van Henle
1.2.2. Anatomie/ histologie ~ functie
ð Hoe complexer de ultrastructuur, hoe groter de actieve rol in de fysiologie!
ð Doorlaatbaarheid neemt af naar distaal toe (strakheid van tight junctions)
1.2.2.1. Glomerulus
• Filtratiebarrière: volledig negatief geladen
• Vaatwand
- Glycocalyx en gefenestreerd endotheel
• Basale membraan
, - 3 lagen: negatief geladen
- Houdt intermediaire en grote moleculen tegen
• Viscerale epitheelwand
- Podocyten met slit poriën, negatief geladen
1.2.2.2. Tubuli
• Proximale tubulus: complexe cellen met veel organellen, brush
border (vooral proximaal)
- Proximale kronkelbuis (PCT): S1 (segment 1) en deel S2
- Proximale rechte tubulus (PST): deel S2 en S3
• Lus van Henle
- Dunne dalende lus van Henle (tDLH): weinig complexe cellen
- Dunne stijgende lus van Henle (tALH): weinig complexe cellen
- Dikke stijgende lus van Henle (TAL): complexe cellen, veel
organellen
• Classical distal tubule
- Distale kronkelbuis (DCT): cellen zoals TAL
- Connecting tubule (CNT):
connecting tubule cells
intercalated cells (zuurbase regeling)
- Initial collecting tubule (ICT)
Intercalated cells (1/3): complexe cellen
Principal cells (2/3): minder complex
• Cortical collecting tubule (CCT)
- Klein stukje van de verzamelbuis in de cortex
• Medullary collecting duct (MCD): minder complex, hoger naar
distaal
- Outer medulla collecting duct (OMCD)
- Inner medulla collecting duct (IMCD)
1.2.2.3. Juxtaglomerulair apparaat
• Lokaal: tubuloglomerlaire feedback
- Hoger aanbod NaCl en vocht aan macula densa (NKCC2
symporter)
- Constrictie van aWerente arteriool met daling van de filtratie
• Systemisch: renine realease
- Daling van druk in nierarterie
- Activatie van baroreceptoren in aWerente arteriool
è vrijzetting van renine uit granulaire cellen (cellen van
ruyter)
- Angiotensinogeen è angiotensine I è angiotensine II
, = systemische vasoconstrictie en aanmaak alodsterone (=
trager proces)
1.2.3. Endocriene functie
ð De nier is ook een endocrien orgaan
ð Renine
- Vrijgezet door granulaire cellen van het juxtaglomerulair apparaat
ð 25-OH-vitamine D
- Omgezet naar 1,25-(OH)2-vitamine D in de proximale tubulus cellen
- Dit is de active vorm, 25-OH-vitD wordt gehydroxyleerd in de proximale
tubulus
ð Erythropoïetine
- Wordt vrijgezet door fibroblast-like cellen in de cortex en outer medulla
- Nier = plaats waar rode bloedcellen gevoeld worden aangezien
bloedtoever 1L/min is (20% van de CO)
ð Prostaglandines
ð Kinines
1.3. Schatting van de globale nierfuncties
Ø 2 grote categorieën (complementair):
- Beeldvormende technieken: echografie, CT, MRI, angiografie, nucleaire
onderzoeken
- Meting van renale klaring
1.3.1. Renale klaring
ð maat voor hoe eWiciënt de nieren het plasma van een stof zuiveren
ð Hoeveelheid plasma waaruit stof volledig verwijderd werd
- Veneuze concentratie = 0
ð Wet van behoud van massa
- Arteriële input = veneuze output + urinaire output
- Px,a. RPFa = Px,v. RPFv + Ux.V
ð Renale klaring voor stof X: Px,v = 0
- Px,a. RPFx,a = (0. RPFv) + (Ux.V)
- Px,a. RPFx,a = Ux.V
!".$
- RPFx,a = Cx = %"&
ð In de meeste gevallen zit er aan de veneuze kant wel nog iets
ð Lage renale klaring: lichaam doet actief moeite om bepaald product bij te
houden
- Lage excretie
- Lichaam houdt deze stof bij
- Bv natrium
Ø Wat doen de nieren?
- Verwijderen metabole producten en toxines uit het bloed
- Homeostatische rol:
Volume-status
Elektrolytenbalans
Zuur-base
- Endocrien: erythrogenese, calcium metabolisme, bloeddruk en bloed flow
Hoofdstuk 1: organisatie van het urinair systeem
1.1. Bloedvoorziening van de nier
Ø Ligging: 12e rib tot 3e lumbale wervel
Ø Gewicht: ± 150 gram
- 0,5% van totale lichaamsgewicht
Ø Bloedvoorziening is hoog!
- 20% van de cardiac output = 1L/min
Ø Einddoel: nefronen
- 800 000 – 1 200 000 per nier
85% oppervlakkige nefronen (cortex)
15% juxta-medullaire nefronen (medulla)
(ó morfologie: andere verdeling nefronen)
- Hoge bloedflow nodig om ultrafiltraat (primair urine) te maken
Ø Bloedvoorziening:
- A renalis – a interlobaris – a arcuata – a interlobularis
- aWerente arteriolen
- Glomerulaire kluwen
- Eferente arteriolen
Peritubulaire capillairen (opp nefronen) - v interlobularis
Vasa recta (juxta-medullaire nefronen)
- Vena arcuata – vena interlobaris – vena renalis
1.2. Het nefron
Ø Glomerulus
- Glomerulaire capillairen
- Mesangium (intra- em extraglomerulair)
- Ruimte em kapsel van Bowman
Ø Tubuli
- Proximale tubulus
,- Lis van Henle
è Oppervlakkige nefronen: kort (tot buitenste deel medulla, bijna geen
stijgend deel)
è Juxtamedullaire nefronen: lang
- Distale tubuli
- Connectie (connecting tubule)
- Verzamelbuisjes: lopen teug helemaal door de medulla tot aan de papil
1.2.1. Fysiologie verschillende delen van het nefron
ð Glomerulus vormt een ultrafiltraat van het plasma (primair urine)
- Samenstelling afhankelijk van de ultrafiltratie coëWiciënt en starling
forces
ð Tubulus bewerkt deze primaire urine
ð Proximale tubulus
- Reabsorptie van water en opgeloste stoWen: NaCl, NaHCO3, glucose,
aminozuren, Ca2+, HPO42, SO42_
- Zuur-base: reabsorptie van HCO3-, secretie NH4+
- Secretie organische anionen en kationen
ð Lus van Henle
- Reabsorptie van NaCl
- Opbouw hypertoniciteit in medulla è nodig voor concentreren
(dilueren) van urine
- Secretie van Tamm-Horsfall glycoproteïne (30-50 mg/dl)
è functie nog onduidelijk: waarschijnljk bescherming tubuli
Kunnen soort cilinder vormen: bloedcellen in cilinder bij patiënten
duidt op een probleem in de lus van Henle
ð Distale tubulus en verzamelbuisjes
- Fine tuning van zout en water excretie afhankelijk van status van het
lichaam
- Wateropname of -secretie op basis van de medullaire hypertoniciteit
opgebouwd in de lus van Henle
1.2.2. Anatomie/ histologie ~ functie
ð Hoe complexer de ultrastructuur, hoe groter de actieve rol in de fysiologie!
ð Doorlaatbaarheid neemt af naar distaal toe (strakheid van tight junctions)
1.2.2.1. Glomerulus
• Filtratiebarrière: volledig negatief geladen
• Vaatwand
- Glycocalyx en gefenestreerd endotheel
• Basale membraan
, - 3 lagen: negatief geladen
- Houdt intermediaire en grote moleculen tegen
• Viscerale epitheelwand
- Podocyten met slit poriën, negatief geladen
1.2.2.2. Tubuli
• Proximale tubulus: complexe cellen met veel organellen, brush
border (vooral proximaal)
- Proximale kronkelbuis (PCT): S1 (segment 1) en deel S2
- Proximale rechte tubulus (PST): deel S2 en S3
• Lus van Henle
- Dunne dalende lus van Henle (tDLH): weinig complexe cellen
- Dunne stijgende lus van Henle (tALH): weinig complexe cellen
- Dikke stijgende lus van Henle (TAL): complexe cellen, veel
organellen
• Classical distal tubule
- Distale kronkelbuis (DCT): cellen zoals TAL
- Connecting tubule (CNT):
connecting tubule cells
intercalated cells (zuurbase regeling)
- Initial collecting tubule (ICT)
Intercalated cells (1/3): complexe cellen
Principal cells (2/3): minder complex
• Cortical collecting tubule (CCT)
- Klein stukje van de verzamelbuis in de cortex
• Medullary collecting duct (MCD): minder complex, hoger naar
distaal
- Outer medulla collecting duct (OMCD)
- Inner medulla collecting duct (IMCD)
1.2.2.3. Juxtaglomerulair apparaat
• Lokaal: tubuloglomerlaire feedback
- Hoger aanbod NaCl en vocht aan macula densa (NKCC2
symporter)
- Constrictie van aWerente arteriool met daling van de filtratie
• Systemisch: renine realease
- Daling van druk in nierarterie
- Activatie van baroreceptoren in aWerente arteriool
è vrijzetting van renine uit granulaire cellen (cellen van
ruyter)
- Angiotensinogeen è angiotensine I è angiotensine II
, = systemische vasoconstrictie en aanmaak alodsterone (=
trager proces)
1.2.3. Endocriene functie
ð De nier is ook een endocrien orgaan
ð Renine
- Vrijgezet door granulaire cellen van het juxtaglomerulair apparaat
ð 25-OH-vitamine D
- Omgezet naar 1,25-(OH)2-vitamine D in de proximale tubulus cellen
- Dit is de active vorm, 25-OH-vitD wordt gehydroxyleerd in de proximale
tubulus
ð Erythropoïetine
- Wordt vrijgezet door fibroblast-like cellen in de cortex en outer medulla
- Nier = plaats waar rode bloedcellen gevoeld worden aangezien
bloedtoever 1L/min is (20% van de CO)
ð Prostaglandines
ð Kinines
1.3. Schatting van de globale nierfuncties
Ø 2 grote categorieën (complementair):
- Beeldvormende technieken: echografie, CT, MRI, angiografie, nucleaire
onderzoeken
- Meting van renale klaring
1.3.1. Renale klaring
ð maat voor hoe eWiciënt de nieren het plasma van een stof zuiveren
ð Hoeveelheid plasma waaruit stof volledig verwijderd werd
- Veneuze concentratie = 0
ð Wet van behoud van massa
- Arteriële input = veneuze output + urinaire output
- Px,a. RPFa = Px,v. RPFv + Ux.V
ð Renale klaring voor stof X: Px,v = 0
- Px,a. RPFx,a = (0. RPFv) + (Ux.V)
- Px,a. RPFx,a = Ux.V
!".$
- RPFx,a = Cx = %"&
ð In de meeste gevallen zit er aan de veneuze kant wel nog iets
ð Lage renale klaring: lichaam doet actief moeite om bepaald product bij te
houden
- Lage excretie
- Lichaam houdt deze stof bij
- Bv natrium