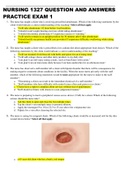
solutions graded A+ 2025/2026
A patient presents with eye pain and blurred vision. Snellen testing reveals vision of 20/200 in
the affected eye and 20/20 in the unaffected eye. Fluorescein staining reveals the presence of a
dendritic ulcer. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Viral keratitis
B. Fungal corneal ulcer
C. Acanthamoeba keratitis
D. Bacterial corneal ulcer - correct answer ✔✔(c) A. Herpes Simplex virus is a common cause of
dendritic ulceration noted on fluorescein staining.
(u) B. Fungal corneal ulcers have an indolent course with intraocular infection being common
but fluorescein staining
is negative for a dendritic pattern.
(u) C. Acanthamoeba keratitis has a waxing and waning course over several months and has no
fluorescein staining
in a dendritic pattern.
(u) D. Bacterial corneal ulcers can progress aggressively resulting in corneal perforation.
Fluorescein staining does
not occur in a dendritic pattern.
A 6 year-old male presents with hemarthrosis of the left knee. Coagulation studies reveal the
following results: PT 12.5 seconds (normal range 12-14 seconds), INR 1.0, aPTT 58 seconds
(normal range 18-28 seconds), platelet count 430,000/microliter (normal range 150,000-
450,000/microliter), and bleeding time 4 minutes (normal range 2-12 minutes). Which of the
following is the best treatment option for this patient?
A. Desmopressin acetate
B. Corticosteroids
,C. Vitamin K
D. Cryoprecipitate - correct answer ✔✔(u) A. Desmopressin acetate is indicated in von
Willebrand's disease, which presents with a prolonged bleeding time.
(u) B. Corticosteroids are indicated in immune-mediated thrombocytopenia.
(u) C. Vitamin K deficiency will prolong the PT greater than the aPTT. Vitamin K supplement is
not indicated in this
patient.
(c) D.Hemophilia A presents with a prolonged aPTT and normal platelet count and function.
Hemophilia A is treated
with factor VIII concentrate or cryoprecipitate.
An HIV positive patient presents with worsening dementia, fever, headache, and right
hemiparesis. MRI of the brain reveals six lesions throughout the brain that show ring
enhancement and surrounding edema. Which of the following is the treatment of choice?
A. Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine
B. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
C. Radiation therapy
D. Ventricular shunt placement - correct answer ✔✔(c) A. Toxoplasmosis is commonly noted in
HIV positive patients and presents with multiple ring-enhancing lesions. Treatment of choice for
possible toxoplasmosis is sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine.
(u) B. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is used for prophylaxis of toxoplasmosis, but not for
treatment of acute infection.
(u) C. Radiation therapy is indicated in CNS lymphoma, which typically presents with a single
lesion.
(u) D. Shunt placement is not indicated in patients with toxoplasmosis.
On examination of a pregnant patient the physician assistant notes a bluish or purplish
discoloration of the vagina and cervix. This is called
A. Hegar's sign.
,B. McDonald's sign.
C. Cullen's sign
D. Chadwick's sign - correct answer ✔✔(u) A. Hegar's sign is the softening of the cervix that
often occurs with pregnancy.
(u) B. McDonald's sign is when the uterus becomes flexible at the uterocervical junction at 7-8
weeks.
(u) C. Cullen's sign is a purplish discoloration periumbilical and noted in pancreatitis.
(c) D. Chadwick's sign is a bluish or purplish discoloration of the vagina and cervix.
A 52 year-old female comes to the office because of black stools for the past 3 days. She is
afebrile and she has no pertinent physical examination abnormalities. Which of the following is
the most appropriate initial diagnostic study?
A. Stool for occult blood
B. Stool cultures
C. Sigmoidoscopy
D. Abdominal CT scan - correct answer ✔✔(c) A. Occult bleeding, as evidenced by the patient's
history of black stools, is initially verified by a positive fecal occult blood test.
(u) B. Stool cultures are indicated in the evaluation of acute diarrhea and not for the evaluation
of acute GI bleeding.
(u) C. Melena suggests a source of bleeding that is proximal to the ligament of Treitz, not a
lower GI bleed.
Sigmoidoscopy is used to evaluate only lower GI bleeding sources.
(u) D. Abdominal CT scan is indicated for evaluation of obscure bleeding in order to exclude a
pancreatic or hepatic
source of bleeding if endoscopy fails to identify the source.
Which of the following is considered a risk factor for the development of malignant melanoma?
A. male gender
B. inability to tan
, C. Japanese ethnicity
D. brown-haired individuals - correct answer ✔✔(u) A. Incidence of malignant melanoma is
equal in males and females.
(c) B. Inability to tan and propensity to burn are risk factors for developing malignant
melanoma.
(u) C. Malignant melanomas are most common in Caucasians and are rarely seen in the
Japanese population. (u) D. Red hair and freckling is one of the major risk factors for malignant
melanoma, not brown hair.
A 43 year-old data entry clerk presents with a one-month history of pain and tingling in the right
thumb, index finger, and middle finger. Tinel's sign and Phalen's maneuver are positive. The
most appropriate intervention at this time is
A. methylprednisolone (Medrol) dose pack.
B. splint in neutral position.
C. observation.
D. surgery. - correct answer ✔✔(u) A. A Medrol dose pack will have no affect on carpal tunnel
syndrome.
(c) B. Splinting in neutral position relieves impingement of the median nerve, thus improving
symptoms of carpal
tunnel.
(u) C. Observation will not improve symptoms.
(u) D. Surgical intervention is reserved for cases unresponsive to conservative therapy.
Which of the following is a cause of prerenal azotemia?
A. Infection
B. Renal toxins
C. Poor renal perfusion
D. Urinary tract obstruction - correct answer ✔✔(u) A. Infection is associated with interstitial
nephritis, which is considered a cause of intrinsic renal azotemia.