University of Vienna
Latest uploads at University of Vienna. Looking for notes at University of Vienna? We have lots of notes, study guides and study notes available for your school.
-
21
-
1
- 0
All courses for University of Vienna
-
Concepts in Molecular Biology 17
-
MP European Law 1
-
Phys 1
-
VO STEOP: Einführung in die Japanologie 150011 1
Latest content University of Vienna

Essential Electrical Quantities in Physics: A Comprehensive Overview covers fundamental concepts and measurements related to electricity within the realm of physics. It implies a thorough examination of key electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, resistance, and others, providing a detailed understanding of their significance and applications in various physical phenomena. This title indicates that the content will serve as a valuable resource for anyone seeking foundational knowledge i...
- Class notes
- • 9 pages's •
-
University of Vienna•Phys
Preview 2 out of 9 pages
Getting your document ready...
Essential Electrical Quantities in Physics: A Comprehensive Overview covers fundamental concepts and measurements related to electricity within the realm of physics. It implies a thorough examination of key electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, resistance, and others, providing a detailed understanding of their significance and applications in various physical phenomena. This title indicates that the content will serve as a valuable resource for anyone seeking foundational knowledge i...

- Genetic diversity - Population genetics Genetic Variation Is a well-adapted population highly homozygous for most favorable alleles? turns out that most populations, even the well adapted ones, have a high degree of heterozygosity across their genomes. How was this realized? the gene for the alcohol dehydrogenase in drosophila, different genes from different subpopulations (1,2,3,4,5) the most common ones were isolated and sequenced and was re...
- Class notes
- • 10 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 10 pages
Getting your document ready...
- Genetic diversity - Population genetics Genetic Variation Is a well-adapted population highly homozygous for most favorable alleles? turns out that most populations, even the well adapted ones, have a high degree of heterozygosity across their genomes. How was this realized? the gene for the alcohol dehydrogenase in drosophila, different genes from different subpopulations (1,2,3,4,5) the most common ones were isolated and sequenced and was re...

GENETIC DIVERSITY AND MEIOSIS I - Introduction to genetics - Mendel rules - Meiosis We are talking about the change of generation and how genetic elements are behaving when they move from one generation to the next. We can think about this how our chromosomes as carries of genetic material and are moving from one generation to ne next, we have somatic cells, generative cells, we are changing between different ploidies and any polyploid organism would have the genetic set prior to the fe...
- Class notes
- • 22 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 3 out of 22 pages
Getting your document ready...
GENETIC DIVERSITY AND MEIOSIS I - Introduction to genetics - Mendel rules - Meiosis We are talking about the change of generation and how genetic elements are behaving when they move from one generation to the next. We can think about this how our chromosomes as carries of genetic material and are moving from one generation to ne next, we have somatic cells, generative cells, we are changing between different ploidies and any polyploid organism would have the genetic set prior to the fe...

This is the process from which one cell divides in two daughter cells, genome information is duplicated and segregated. There are different stages in mitosis: - chromosome condensation in profase, nuclear envelope breakdown which brings you into pro-metaphase at which point the chromosomes are starting to align on the mitotic spindle that is alreading forming on the outside of the nucleous. - In metaphase there is an align state; once the cell has conformed that indeed al the chromosomes ar...
- Class notes
- • 21 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 3 out of 21 pages
Getting your document ready...
This is the process from which one cell divides in two daughter cells, genome information is duplicated and segregated. There are different stages in mitosis: - chromosome condensation in profase, nuclear envelope breakdown which brings you into pro-metaphase at which point the chromosomes are starting to align on the mitotic spindle that is alreading forming on the outside of the nucleous. - In metaphase there is an align state; once the cell has conformed that indeed al the chromosomes ar...
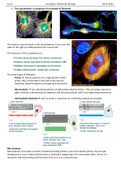
The actine is concentrated in the cell periphery, in this case the cells on the right are differentiated into neural cells. The functions of the cytoskeleton is: The three types of filaments: - Actine helical polimers of a single protein called actine, they concentrate in the cell cortex and are important determining the cell shape and movement - Microtubules are cylindrical polimers of alpha-beta tubuline dimers. They are larger and more rigid, involved in positioning cell org...
- Class notes
- • 17 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 3 out of 17 pages
Getting your document ready...
The actine is concentrated in the cell periphery, in this case the cells on the right are differentiated into neural cells. The functions of the cytoskeleton is: The three types of filaments: - Actine helical polimers of a single protein called actine, they concentrate in the cell cortex and are important determining the cell shape and movement - Microtubules are cylindrical polimers of alpha-beta tubuline dimers. They are larger and more rigid, involved in positioning cell org...

Last time we said that the problem we are discussing is how cells manage to create different compartments; procaryotes and eukaryotes have major differences in complexity, and the major innovation in this transition is the nucleus, the invention of a new compartment that allows cells to carry out certain functions in a different compartment (gene transcription) and physically separated from translation that happens in the cytoplasm. Doing so, creates regulatory layers that otherwise would not be...
- Class notes
- • 9 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 9 pages
Getting your document ready...
Last time we said that the problem we are discussing is how cells manage to create different compartments; procaryotes and eukaryotes have major differences in complexity, and the major innovation in this transition is the nucleus, the invention of a new compartment that allows cells to carry out certain functions in a different compartment (gene transcription) and physically separated from translation that happens in the cytoplasm. Doing so, creates regulatory layers that otherwise would not be...

How is the densely packed cellular space organized to enable control over complex biochemical reactions in space and time? In cells we do have compartments, such as the largest one: ER the endoplasmic reticulum, a classic form of membrane bound organelle which is fully formed by a bilayer membrane. ER has different compartments and we infer these differences because these compartments have different shapes: - Smooth ER - Rough ER, with ribosomes. - Nucleus and ER are treated as differe...
- Class notes
- • 14 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 14 pages
Getting your document ready...
How is the densely packed cellular space organized to enable control over complex biochemical reactions in space and time? In cells we do have compartments, such as the largest one: ER the endoplasmic reticulum, a classic form of membrane bound organelle which is fully formed by a bilayer membrane. ER has different compartments and we infer these differences because these compartments have different shapes: - Smooth ER - Rough ER, with ribosomes. - Nucleus and ER are treated as differe...
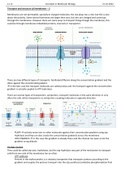
Transport and structure of membranes – 2 Membranes are not permeable, specially to charged molecules, the size plays too a role, but this is also about the polarity. Some steroid hormones are larger then ions, but ions are charged and cannot go through the membranes. However there are some ways to transport things though the membrane, this could be through membrane embedded proteins, channels or transporter. There are two different types of transports: ...
- Class notes
- • 13 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 13 pages
Getting your document ready...
Transport and structure of membranes – 2 Membranes are not permeable, specially to charged molecules, the size plays too a role, but this is also about the polarity. Some steroid hormones are larger then ions, but ions are charged and cannot go through the membranes. However there are some ways to transport things though the membrane, this could be through membrane embedded proteins, channels or transporter. There are two different types of transports: ...

Transport and structure of membranes Amphiphilic lipids spontaneously form micelles and bilayers The major classes of the lipids are amphiphilic, having a hydrophobic part (typically a fatty acid, saturated or not) and a hydrophilic cater group. o Glycerophospholipid they glicerin is acilated in sn1 and sn2 position; the sn3 position gets phosphorylated and could carry and additional head group. The acil chains on the other hand are hidrophobic o Sphingosine a primary alcohol ...
- Class notes
- • 12 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 12 pages
Getting your document ready...
Transport and structure of membranes Amphiphilic lipids spontaneously form micelles and bilayers The major classes of the lipids are amphiphilic, having a hydrophobic part (typically a fatty acid, saturated or not) and a hydrophilic cater group. o Glycerophospholipid they glicerin is acilated in sn1 and sn2 position; the sn3 position gets phosphorylated and could carry and additional head group. The acil chains on the other hand are hidrophobic o Sphingosine a primary alcohol ...

When we’ll be talking about autophagy, we’ll refer to macroautophagy which is characterized by the formation of a membrane structure called isolation membrane, its forms next to the ER endoplasmic reticulum but its not a continuation or extension of it, it’s a membrane structure that’s form de novo. This membrane structure grows in 3 dimensions, while growing it encapsulates cytoplasmic cargo material and then when the isolation membrane encloses, by a fission reaction, results in two fi...
- Class notes
- • 14 pages's •
-
University Of Vienna•Concepts in Molecular Biology
Preview 2 out of 14 pages
Getting your document ready...
When we’ll be talking about autophagy, we’ll refer to macroautophagy which is characterized by the formation of a membrane structure called isolation membrane, its forms next to the ER endoplasmic reticulum but its not a continuation or extension of it, it’s a membrane structure that’s form de novo. This membrane structure grows in 3 dimensions, while growing it encapsulates cytoplasmic cargo material and then when the isolation membrane encloses, by a fission reaction, results in two fi...
