12 class
Latest uploads at 12 class. Looking for notes at 12 class? We have lots of notes, study guides and study notes available for your school.
-
237
- 0
-
5
All courses for 12 class
Latest content 12 class

Oxidation state (oxidation number) represents the apparent charge of an atom in a compound, indicating electron gain or loss. It follows specific rules: free elements have an oxidation state of zero, oxygen is usually -2 (except in peroxides: -1), and hydrogen is +1 (except in metal hydrides: -1). The sum of oxidation states in a neutral compound is zero, while in ions, it equals the ion’s charge. Transition elements show variable oxidation states due to partially filled d-orbitals. Oxidation ...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
Getting your document ready...
Oxidation state (oxidation number) represents the apparent charge of an atom in a compound, indicating electron gain or loss. It follows specific rules: free elements have an oxidation state of zero, oxygen is usually -2 (except in peroxides: -1), and hydrogen is +1 (except in metal hydrides: -1). The sum of oxidation states in a neutral compound is zero, while in ions, it equals the ion’s charge. Transition elements show variable oxidation states due to partially filled d-orbitals. Oxidation ...

Electronic configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals based on the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Electrons fill orbitals in increasing energy order: 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p, and so on. Elements in the same group have similar valence shell configurations, explaining periodic properties. Transition and inner transition elements show exceptions due to stability factors like half-filled and full...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
Getting your document ready...
Electronic configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals based on the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Electrons fill orbitals in increasing energy order: 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p, and so on. Elements in the same group have similar valence shell configurations, explaining periodic properties. Transition and inner transition elements show exceptions due to stability factors like half-filled and full...

Atomic and ionic sizes refer to the radii of atoms and ions. Atomic size increases down a group due to added electron shells but decreases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer. Ionic size depends on charge: cations are smaller than their parent atoms due to electron loss and increased nuclear attraction, while anions are larger due to electron gain and increased electron-electron repulsion. Transition metals show irregular trends due to d-orbital contrac...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
Getting your document ready...
Atomic and ionic sizes refer to the radii of atoms and ions. Atomic size increases down a group due to added electron shells but decreases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer. Ionic size depends on charge: cations are smaller than their parent atoms due to electron loss and increased nuclear attraction, while anions are larger due to electron gain and increased electron-electron repulsion. Transition metals show irregular trends due to d-orbital contrac...
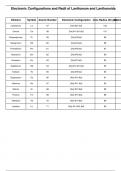
The lanthanides, also known as rare earth elements, include 15 elements from lanthanum (La) to lutetium (Lu). Their electron configurations typically follow the filling of the 4f orbitals, though exceptions exist due to electron stability considerations. These elements exhibit similar chemical properties due to their common +3 oxidation state. Across the series, the atomic and ionic radii decrease, a trend known as the lanthanide contraction, caused by poor shielding of nuclear charge by 4f elec...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 1 pages
Getting your document ready...
The lanthanides, also known as rare earth elements, include 15 elements from lanthanum (La) to lutetium (Lu). Their electron configurations typically follow the filling of the 4f orbitals, though exceptions exist due to electron stability considerations. These elements exhibit similar chemical properties due to their common +3 oxidation state. Across the series, the atomic and ionic radii decrease, a trend known as the lanthanide contraction, caused by poor shielding of nuclear charge by 4f elec...

The general characteristics of elements in Class 12 Chemistry focus on periodic trends, electronic configurations, oxidation states, and reactivity patterns. Transition elements (d-block) exhibit variable oxidation states, form colored compounds, and show catalytic and magnetic properties. Inner transition elements (f-block) include lanthanoids and actinoids, known for their high reactivity and radioactive nature (actinoids). Key topics include ionization energy, atomic size, complex formation, ...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
Getting your document ready...
The general characteristics of elements in Class 12 Chemistry focus on periodic trends, electronic configurations, oxidation states, and reactivity patterns. Transition elements (d-block) exhibit variable oxidation states, form colored compounds, and show catalytic and magnetic properties. Inner transition elements (f-block) include lanthanoids and actinoids, known for their high reactivity and radioactive nature (actinoids). Key topics include ionization energy, atomic size, complex formation, ...

The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry chapter on d- and f-block elements covers the properties, trends, and applications of transition and inner transition metals. It explains their variable oxidation states, catalytic properties, complex formation, and colored ions due to d-d transitions. The lanthanoids and actinoids show unique electronic configurations and chemical reactivity. Important topics include magnetic properties, alloy formation, and industrial applications (e.g., catalysts, pigments, and sup...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 17 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 3 out of 17 pages
Getting your document ready...
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry chapter on d- and f-block elements covers the properties, trends, and applications of transition and inner transition metals. It explains their variable oxidation states, catalytic properties, complex formation, and colored ions due to d-d transitions. The lanthanoids and actinoids show unique electronic configurations and chemical reactivity. Important topics include magnetic properties, alloy formation, and industrial applications (e.g., catalysts, pigments, and sup...

The formation of colored ions, especially in transition metals, results from electronic transitions within partially filled d-orbitals. When light interacts with these ions, certain wavelengths are absorbed, causing d-d transitions, where electrons jump between split d-orbital energy levels. The remaining wavelengths determine the observed color. Factors influencing color include the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination geometry, explained by crystal field theory. Higher oxid...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 1 pages
Getting your document ready...
The formation of colored ions, especially in transition metals, results from electronic transitions within partially filled d-orbitals. When light interacts with these ions, certain wavelengths are absorbed, causing d-d transitions, where electrons jump between split d-orbital energy levels. The remaining wavelengths determine the observed color. Factors influencing color include the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination geometry, explained by crystal field theory. Higher oxid...
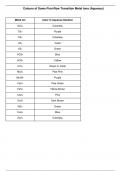
The colors of transition metal ions arise from electronic transitions within the d-orbitals, influenced by the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination environment. In these ions, partially filled d-orbitals allow for d-d transitions, where electrons absorb specific wavelengths of light and move between energy levels, with the remaining light determining the observed color. The crystal field theory explains how ligands split d-orbital energy levels, affecting color intensity. Com...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 1 pages
Getting your document ready...
The colors of transition metal ions arise from electronic transitions within the d-orbitals, influenced by the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination environment. In these ions, partially filled d-orbitals allow for d-d transitions, where electrons absorb specific wavelengths of light and move between energy levels, with the remaining light determining the observed color. The crystal field theory explains how ligands split d-orbital energy levels, affecting color intensity. Com...

The formation of complex compounds involves the coordination of a central metal ion with surrounding ligands through coordinate covalent bonds. These ligands, which can be neutral molecules or anions, donate electron pairs to the metal, forming a stable structure known as a coordination complex. Factors influencing complex formation include the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination number. Complex compounds exhibit unique properties like color, magnetism, and catalytic activit...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
Getting your document ready...
The formation of complex compounds involves the coordination of a central metal ion with surrounding ligands through coordinate covalent bonds. These ligands, which can be neutral molecules or anions, donate electron pairs to the metal, forming a stable structure known as a coordination complex. Factors influencing complex formation include the metal’s oxidation state, ligand type, and coordination number. Complex compounds exhibit unique properties like color, magnetism, and catalytic activit...

Catalytic properties refer to the ability of a substance, known as a catalyst, to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Catalysts lower activation energy, enhancing reaction rates while remaining unchanged. They can be homogeneous (same phase as reactants) or heterogeneous (different phase). Enzymes, a type of biological catalyst, facilitate biochemical reactions. Catalysts are essential in industrial processes like petroleum refining, polymer production, and envir...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages's •
-
12 class•12 class
-
NCERT Examplar Chemistry Class 12th • Ramashish Paul• ISBN 9789351764649
Preview 1 out of 1 pages
Getting your document ready...
Catalytic properties refer to the ability of a substance, known as a catalyst, to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Catalysts lower activation energy, enhancing reaction rates while remaining unchanged. They can be homogeneous (same phase as reactants) or heterogeneous (different phase). Enzymes, a type of biological catalyst, facilitate biochemical reactions. Catalysts are essential in industrial processes like petroleum refining, polymer production, and envir...
