Save
Students also studied
Chapter 29- Chest and Abdominal Tr... Chapter 21 Test Ch. 22 Study Guide
348 terms 24 terms 32 terms
anaphylacticshock Preview kenanderson2017 Preview Kendall_Dinning
Terms in this set (51)
What is the heart? The muscle responsible for the process by which blood is
pumped throughout the body.
Pericardium The layer or sac that surrounds the heart.
Myocardium The middle layer of heart muscle.
Endocardium The innermost layer of heart muscle.
Epicardium The top layer of heart muscle.
Conduction System of the Heart The system responsible for the regulation of the pumping
action of the heart, as well as the conduction of the electrical
impulses that causes the myocardium to contract.
Conduction system pathway Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, Bundle of His,
right and left bundle branches, purkinje fibers
Myocardial infarction Commonly known as a heart attack, is a term that refers to an
obstruction to the myocardial tissue. This obstruction causes
an interruption of the blood supply to part of the heart which
causes the heart cells to die.
Myocardial ischemia Also known as angina, is a condition caused by a lack of
oxygen-rich blood in the heart.
Arrhythmia A term used to refer to any disorder of your heart rate or
rhythm.
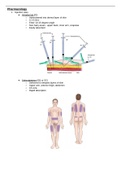
, Limb Leads 1. Lead I: Records electrical activity from right arm to left arm
2. Lead II: Records electrical activity from right arm to left leg
3. Lead III: Records electrical activity from left arm to left leg
Augmented Leads 1. aVR: Records electrical activity away from midpoint between
left arm and left leg to right arm (across heart to right
shoulder)
2. aVL: Records electrical activity from midpoint between right
arm and left leg to left arm (across heart to left shoulder)
3. aVF: Records electrical activity from midpoint between right
arm and left arm to left leg (across heart toward feet)
Chest or Precordial Leads 1. V1: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V1 electrode is placed
2. V2: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V2 electrode is placed
3. V3: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V3 electrode is placed
4. V4: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V4 electrode is placed
5. V5: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V5 electrode is placed
6. V6: Records electrical activity between center of heart and
the chest wall where V6 electrode is placed
Isoelectric line A term used to describe a straight line on the ECG strip with
illustrates the resting state of the myocardial cells.
The Five Steps for Analyzing an ECG Heart rate, regularity, P-waves, QRS complex, and P-R interval.
The 6 Second Interval x 10 Method This involves counting the number of QRS complexes on a 6
second rhythm and multiplying that number by 10, this is the
only method that can be used on an irregular rhythm.
The 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 Method. This involves locating an R-wave on a bold line on the ECG
paper then finding the next consecutive R wave and counting
down from 300 on the subsequent bold lines to determine the
rate.
1500 Method Count number of small squares between two consecutive R-
waves and divide that number by 1500, it is the most accurate
method of obtaining the heart rate but can only be used on
regular rhythms.