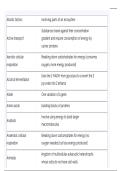
Abiotic factors nonliving parts of an ecosystem
Substances travel against their concentration
Active transport gradient and require consumption of energy by
carrier proteins
Aerobic cellular Breaking down carbohydrates for energy (consumes
respiration oxygen, more energy produced)
Uses the 2 NADH from glycolysis to convert the 2
Alcohol fermentation
pyruvate into 2 ethanol
Allele One variation of a gene
Amino acids building blocks of proteins
Involve using energy to build larger
Anabolic
macromolecules
Anaerobic cellular Breaking down carbohydrates for energy (no
respiration oxygen needed, but less energy produced)
kingdom of multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs
Animalia
whose cells do not have cell walls
, known as protozoa, have food vacuoles. Include
Animal-like protists amoeba and paramecium. Heterotrophic (move via
flagella and cilia) and often parasitic pathogens.
Apparent competition Occurs when one predator preys on two species
Cell wall lacks peptidoglycan, lipids bound via
Archaea ether-linkages
Extremophiles: able to survive harsh environments
used as the cellular energy currency because of the
ATP
high energy bonds between the phosphate groups
A channel protein that provides a hydrophilic tunnel
ATP synthase to allow protons to flow down their electrochemical
gradient
The breakdown of the cell's own machinery for
Autophagy
recycling
Autosomes 22 pairs in the human body; nonsex chromosomes
Autotrophs Make their own food
, Organisms will replicate their genome while cell
Binary fission
division is happening
All ecosystems on earth, their interactions with each
Biosphere other and the lithosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere,
atmospher
Biotic factors Living elements of an ecosystem
light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis in
Calvin cycle which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build
high-energy compounds such as sugar
Capillary action an adhesive force pulls water column upward
contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Carbohydrates Come in forms of monosaccharides, disaccharides,
and polysaccharides
Process by which inorganic carbon is converted into
Carbon fixation
an organic molecule
Substances travel against their concentration
Active transport gradient and require consumption of energy by
carrier proteins
Aerobic cellular Breaking down carbohydrates for energy (consumes
respiration oxygen, more energy produced)
Uses the 2 NADH from glycolysis to convert the 2
Alcohol fermentation
pyruvate into 2 ethanol
Allele One variation of a gene
Amino acids building blocks of proteins
Involve using energy to build larger
Anabolic
macromolecules
Anaerobic cellular Breaking down carbohydrates for energy (no
respiration oxygen needed, but less energy produced)
kingdom of multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs
Animalia
whose cells do not have cell walls
, known as protozoa, have food vacuoles. Include
Animal-like protists amoeba and paramecium. Heterotrophic (move via
flagella and cilia) and often parasitic pathogens.
Apparent competition Occurs when one predator preys on two species
Cell wall lacks peptidoglycan, lipids bound via
Archaea ether-linkages
Extremophiles: able to survive harsh environments
used as the cellular energy currency because of the
ATP
high energy bonds between the phosphate groups
A channel protein that provides a hydrophilic tunnel
ATP synthase to allow protons to flow down their electrochemical
gradient
The breakdown of the cell's own machinery for
Autophagy
recycling
Autosomes 22 pairs in the human body; nonsex chromosomes
Autotrophs Make their own food
, Organisms will replicate their genome while cell
Binary fission
division is happening
All ecosystems on earth, their interactions with each
Biosphere other and the lithosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere,
atmospher
Biotic factors Living elements of an ecosystem
light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis in
Calvin cycle which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build
high-energy compounds such as sugar
Capillary action an adhesive force pulls water column upward
contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Carbohydrates Come in forms of monosaccharides, disaccharides,
and polysaccharides
Process by which inorganic carbon is converted into
Carbon fixation
an organic molecule