GUIDE 2026 COMPLETE QUESTIONS WITH
CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS || 100%
GUARANTEED PASS <RECENT VERSION>
PNB 2274 - Comprehensive Lab Practical 2 Study Guide
Focus Areas: Nervous System, Special Senses, Endocrine, Muscles, Cardiovascular, &
Respiratory Physiology
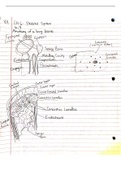
Section 1: Nervous System Anatomy & Histology
1. Q: Identify the structure pointed to on a model of a neuron (e.g., axon hillock, dendrite,
myelin sheath). What is its primary function?
A: Axon Hillock. Its function is to integrate incoming graded potentials from the
dendrites and soma. If the summation reaches threshold at the axon hillock, it initiates
an action potential.
2. Q: On a cross-section of the spinal cord, differentiate between the dorsal and ventral
horns. What type of neurons are found in each?
A: Dorsal horns contain the cell bodies of interneurons and sensory processing
neurons. Ventral horns contain the cell bodies of somatic motor neurons that send
axons out to skeletal muscles.
3. Q: You view a slide under the microscope showing clusters of neuron cell bodies
surrounded by axons. Are you looking at gray matter or white matter in the CNS?
A: Gray matter. Gray matter consists primarily of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and
unmyelinated axons. White matter consists of bundles of myelinated axons (tracts).
4. Q: What are the three meningeal layers from superficial to deep? Identify them on a
model.
A: Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater.
5. Q: (Station with brain model) Identify the longitudinal fissure. What does it separate?
A: The deep groove running front-to-back along the midline. It separates the two
cerebral hemispheres.
, 6. Q: What is the primary function of the cerebellum, identifiable by its foliated (leaf-like)
appearance?
A: Coordination of voluntary movement, balance, equilibrium, and fine motor control
(motor learning).
7. Q: Which ventricle is located between the brainstem and the cerebellum?
A: The fourth ventricle.
8. Q: Damage to which major brain region (visible on the ventral surface) would affect basic
life functions like heart rate and respiration?
A: The medulla oblongata.
Section 2: Neurophysiology & Reflexes
9. Q: During an action potential, what ion rushes into the cell to cause the depolarization
phase?
A: Sodium ions (Na+).
10. Q: What is the period immediately following an action potential where a new action
potential cannot be generated, no matter how strong the stimulus?
A: The absolute refractory period.
11. Q: In a chemical synapse, what do we call the gap between the pre- and post-synaptic
neurons?
A: The synaptic cleft.
12. Q: You test the patellar reflex. What is the sensory receptor, and what type of reflex is
this?
A: Muscle spindle (stretch receptor). It is a monosynaptic stretch reflex.
13. Q: What would be the expected result if you damaged the motor neuron of a reflex arc?
A: The reflex would be absent or diminished because the efferent signal cannot reach
the effector organ (muscle).
14. Q: On an oscilloscope readout of a nerve conduction experiment, what does the latency
period represent?
A: The time between the stimulus application and the beginning of the recorded
response. It includes conduction time along the nerve and synaptic delays.
Section 3: Special Senses (Vision, Hearing, Balance, Taste/Smell)
, 15. Q: (Station with eye model) Identify the structure that changes shape to focus light on
the retina.
A: The lens (accommodation is performed by the ciliary muscle).
16. Q: Which photoreceptor cells are responsible for vision in low-light conditions (scotopic
vision)?
A: Rods.
17. Q: What is the name of the "blind spot" on the retina, and why is it blind?
A: The optic disc. It is blind because it contains no photoreceptors; it is where the optic
nerve and blood vessels exit the eye.
18. Q: (Station with ear model) Identify the three ossicles in the middle ear from lateral to
medial.
A: Malleus, Incus, Stapes.
19. Q: The cochlea is responsible for hearing. What specific structure within the cochlea
contains the hair cells for sound transduction?
A: The Organ of Corti (located on the basilar membrane).
20. Q: What are the two functional types of hair cells in the vestibular system, and what do
they detect?
A: Maculae (in saccule & utricle) detect linear acceleration and head position relative to
gravity. Cristae ampullares (in semicircular canals) detect rotational/angular
acceleration.
21. Q: During a Rinne test, if air conduction (AC) is greater than bone conduction (BC) but
both are reduced, what is the likely diagnosis?
A: Sensorineural hearing loss. (If BC > AC, it indicates conductive hearing loss).
Section 4: Endocrine System
22. Q: On a model, identify the "master gland" that regulates other endocrine glands.
A: The pituitary gland (hypophysis).
23. Q: Which hormone, released from the posterior pituitary, is responsible for water
retention in the kidneys?
A: Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH or Vasopressin).
24. Q: The Islets of Langerhans are found in which endocrine gland? Name one hormone
they secrete.
A: The pancreas. They secrete insulin (beta cells) or glucagon (alpha cells).