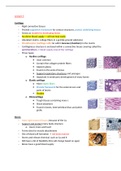
Mapping and Inverse functions
Mapping, functions and non-functions
Functions and non-functions:
Function
= a relationship between 2 sets, A and B, where every element of A (the input set) is mapped
onto only one element of B (the output set).
That means: for every x value there is an unique y-value.
No two ordered pairs will have the same x-value. – x not repeated
Non-function
= a relationship between 2 sets, A and B, where an element of A (the input set) is mapped onto
more than one element of B (the output set).
That means: for every x value there can be more than one y-value.
Two ordered pairs will have the same x-value. – x repeated
Mapping:
Type 1: … to function (one)
. One-to-One mapping
. Each element of the domain is mapped onto an unique value of y.
. (x is not repeated, neither is y)
Type 2: … to function (one)
. Many-to-One mapping
. Each element of the domain is mapped onto only 1 value of y.
. (x is not repeated, but y could be)
Type 3: … to non-function (many)
. One-to-Many mapping
. An element of the domain can be mapped onto many different elements of the range.
. (x is repeated, but y is not)
Type 4: … to non-function (many)
. Many-to-Many mapping
. Many elements of the domain can be mapped onto many elements of the range.
. (x is repeated, so is y).
, Determining “to-one” or “to many”
= determine if a function or non-function ∴ the vertical line test
A vertical line has equation x =, so every point on a vertical line has the same x-value.
Process = Move a vertical line across the graph.
. In how many points does this line cut the graph?
1 point only – Function ∴ to one
More than 1 – Non function∴ to many
Determining “one-to” or “many-to”
= the horizontal line test
A horizontal line has equation y =, so every point on a horizontal line has the same y-value.
Process = Move a horizontal line across the graph.
. In how many points does this line cut the graph?
1 point only – one to
More than 1 – many to
Inverses
- Multiplicative inverses = two numbers multiplied to get 1
- Additive inverses = two numbers added to get 0
Inverse function = a reflection in the line y = x.
(x ; y) (y ; x)
The inverse of a function f, written as f -1.
NOTE: f (function); f’ (derivative); f-1 (inverse)
Finding the inverse:
1. Get the formula into standard form. (y = …)
2. Swap x and y.
3. Solve so that y is the subject of the formula.
e.g. f. y = 3x – 4
. f-1. x = 3y – 4
. 3y = x + 4
𝑥+4
. y= 3
e.g. f. y = 3x2
. f-1. x = 3y2
𝑥
. y = ± √3
Mapping, functions and non-functions
Functions and non-functions:
Function
= a relationship between 2 sets, A and B, where every element of A (the input set) is mapped
onto only one element of B (the output set).
That means: for every x value there is an unique y-value.
No two ordered pairs will have the same x-value. – x not repeated
Non-function
= a relationship between 2 sets, A and B, where an element of A (the input set) is mapped onto
more than one element of B (the output set).
That means: for every x value there can be more than one y-value.
Two ordered pairs will have the same x-value. – x repeated
Mapping:
Type 1: … to function (one)
. One-to-One mapping
. Each element of the domain is mapped onto an unique value of y.
. (x is not repeated, neither is y)
Type 2: … to function (one)
. Many-to-One mapping
. Each element of the domain is mapped onto only 1 value of y.
. (x is not repeated, but y could be)
Type 3: … to non-function (many)
. One-to-Many mapping
. An element of the domain can be mapped onto many different elements of the range.
. (x is repeated, but y is not)
Type 4: … to non-function (many)
. Many-to-Many mapping
. Many elements of the domain can be mapped onto many elements of the range.
. (x is repeated, so is y).
, Determining “to-one” or “to many”
= determine if a function or non-function ∴ the vertical line test
A vertical line has equation x =, so every point on a vertical line has the same x-value.
Process = Move a vertical line across the graph.
. In how many points does this line cut the graph?
1 point only – Function ∴ to one
More than 1 – Non function∴ to many
Determining “one-to” or “many-to”
= the horizontal line test
A horizontal line has equation y =, so every point on a horizontal line has the same y-value.
Process = Move a horizontal line across the graph.
. In how many points does this line cut the graph?
1 point only – one to
More than 1 – many to
Inverses
- Multiplicative inverses = two numbers multiplied to get 1
- Additive inverses = two numbers added to get 0
Inverse function = a reflection in the line y = x.
(x ; y) (y ; x)
The inverse of a function f, written as f -1.
NOTE: f (function); f’ (derivative); f-1 (inverse)
Finding the inverse:
1. Get the formula into standard form. (y = …)
2. Swap x and y.
3. Solve so that y is the subject of the formula.
e.g. f. y = 3x – 4
. f-1. x = 3y – 4
. 3y = x + 4
𝑥+4
. y= 3
e.g. f. y = 3x2
. f-1. x = 3y2
𝑥
. y = ± √3