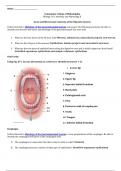
CORRECTLY UPGRADED AND DETAILED
1. substrate: substance on which a catalyst works
2. enzyme: biologic catalyst; protein in nature
3. catalyst: increases chemical reaction rate without becoming part of the product
4. control: provides a standard of comparison for test results
5. Salivary amylase: produced by salivary
glands located in the mouth
substrates: starch
optimal pH = 6.7-7
6. Trypsin: produced by
pancreas works in the small
intestine substrates: protein
(polypeptides) optimal pH = 8
7. Lipase (pancreatic): produced by
pancreas works in the small intestine
substrates: lipids (fats)
optimal pH = 7.4-8
8. Name 3 digestive enzymes: salivary
amylase trypsin
lipase (pancreatic)
9. List 4 types of indicators:
BAPNA Lugol's iodine (IKI)
Litmus
Benedict's Solution
10. BAPNA: tests for protein hydrolysis (yellow color)
11. Lugol's Iodine (IKI): tests for presence of starch (blue-black color)
12. Litmus: tests for presence of fatty acids (blue to pink)
13. Benedict's Solution: tests for presence of reducing sugars (maltose, sucrose,
glucose) (blue to green; orange)
14. 5 Types of Substances:
monosaccharides fatty acids/
monoglycerides
amino acids
1/
2