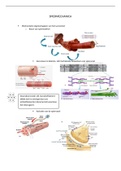
Recombinant DNA technology I (KCSPK20) • Multiplication occurs in host cells
• Cloned DNA can be recovered, purified and analyzed
This chapter will introduce the principles and basic techniques
used in recombinant DNA technology THUS: Cut, Paste and Copy!
This chapter will be presented in 6 lectures: Restriction enzymes (molecular scissors)
REs are important tools in recombinant DNA technology
1. Basic tools – restriction enzymes and cloning vectors
2. DNA libraries • Endonucleases (antiviral protection against phages) –
3. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) produced by bacteria
4. Techniques for analyzing nucleic acids • Type I (cut DNA far from recognition site) and II (cut DNA at
5. DNA sequencing the recognition site)
6. Transgenics and knockouts • > 500 commercial REs
Recombinant DNA technology (Genetic engineering) • Palindromic recognition sequences
• Generate restriction fragments
• Based on the cutting and pasting of DNA molecules at
• Frequent vs. rare cutters
specific base sequences
• Sticky (cohesive) vs. blunt ends
• Resulting DNA fragment can be transferred from any
organism to a virus or bacterial cell in order to mass- palindrome
produce, isolate and characterize it
• Used for gene mapping, diagnosis of diseases, commercial
production of human gene products and the expression of
foreign genes in transgenic animals and plants
• First commercial “biotech product” – Insulin (1982)
Making recombinant DNA
The process comprises a series of steps
• DNA is isolated from cells
• DNA is cut by restriction enzymes (REs)
• Fragments are ligated into “vectors”
• Recombinant molecules are transformed into host cells
, What is a palindrome / palindromic sequence? Restriction enzymes
Same sequence on both strands in the same direction
Overhangs can anneal to complementary sequence by hydrogen bonds
Restriction enzymes “straight cut” – more di`icult to ligate, less used
6-nt sites
6-nt sites
4-nt sites
4-nt sites
Restriction enzymes – what’s in a name? HindIII cuts DNA every 4096 bp (in theory)
Alul cuts DNA every 256 bp (in theory)
, Creating a recombinant DNA molecule • Types: plasmids, phages, cosmids, shuttles, BACs and
Restriction site Restriction site YACs
DNA from DNA form
source 1 source 2
Sticky end after
digestion with EcoRI
Sticky end after
digestion with EcoRI
Hydrogen bonds are
formed but there are
nicks in the backbone
“Famous plasmids”
Ligase restores F plasmid in E. coli (fertility/conjugation)
phosphodiester bonds R plasmids carrying antibiotic resistance genes
Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens (used in plant genetic engineering
Plasmids
Vectors Small, extrachromosomal DNA molecules within a cell (e.g.
Another important tool in recombinant DNA bacterium) that are physically separated from chromosomal
DNA and can replicate independently. The cell’s machinery
• ” Vehicle” to get DNA into host cell (transformation)
expresses the plasmid’s genes
• Prerequisites:
- Must be able to replicate autonomously (ori+) – DNA • Natural, self-replicating, extra-chromosomal
replication site • Small circular DNA molecule that functions independently
- Contain various unique RE sites from the host cell (autonomous replication)
- Selectable marker (AbR) -antibiotic resistance • Modified to contain an MCS/polylinker
- Should be easy to recover from host cell • Contains AbR selectable marker gene – for distinguishing
between cells that have taken up the vector
, • High copy number (+/- 1000) Insertional inactivation
• Proper MCS in lac Z (insertional inactivation) – inactivates
LacZ
• +/- 20 kb inserts
Modified to contain an MCS/polylinker
Contains AbR
selectable marker
gene
Typical DNA cloning plasmid Proper MCS in lac Z (insertional
inactivation)
Cloning in bacterial cells Blue/white selection
• ß-galactosidase catalyzes the conversion of the X-GAL
substrate to form a bright blue precipitate
• No insertion means the ß-galactosidase enzyme is
Plasmid it cut
functional, thus a blue precipitate forms
with RE Source DNA to be cloned is cut
• Insertion of a cloned DNA fragment disrupt the lac Z ORF,
with the same RE
thus ß-galactosidase is inactivated, and no blue color
visible
Ligation produces recombinant plasmid
Blue colonies – functional LacZ – non-recombinant plasmid
Transformation of bacterial White colonies – non-functional LacZ – recombinant plasmid
cells (electroporation or
calcium + heat shock)
Selection of transformed bacterial cells by antibiotic / X-gal
• Cloned DNA can be recovered, purified and analyzed
This chapter will introduce the principles and basic techniques
used in recombinant DNA technology THUS: Cut, Paste and Copy!
This chapter will be presented in 6 lectures: Restriction enzymes (molecular scissors)
REs are important tools in recombinant DNA technology
1. Basic tools – restriction enzymes and cloning vectors
2. DNA libraries • Endonucleases (antiviral protection against phages) –
3. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) produced by bacteria
4. Techniques for analyzing nucleic acids • Type I (cut DNA far from recognition site) and II (cut DNA at
5. DNA sequencing the recognition site)
6. Transgenics and knockouts • > 500 commercial REs
Recombinant DNA technology (Genetic engineering) • Palindromic recognition sequences
• Generate restriction fragments
• Based on the cutting and pasting of DNA molecules at
• Frequent vs. rare cutters
specific base sequences
• Sticky (cohesive) vs. blunt ends
• Resulting DNA fragment can be transferred from any
organism to a virus or bacterial cell in order to mass- palindrome
produce, isolate and characterize it
• Used for gene mapping, diagnosis of diseases, commercial
production of human gene products and the expression of
foreign genes in transgenic animals and plants
• First commercial “biotech product” – Insulin (1982)
Making recombinant DNA
The process comprises a series of steps
• DNA is isolated from cells
• DNA is cut by restriction enzymes (REs)
• Fragments are ligated into “vectors”
• Recombinant molecules are transformed into host cells
, What is a palindrome / palindromic sequence? Restriction enzymes
Same sequence on both strands in the same direction
Overhangs can anneal to complementary sequence by hydrogen bonds
Restriction enzymes “straight cut” – more di`icult to ligate, less used
6-nt sites
6-nt sites
4-nt sites
4-nt sites
Restriction enzymes – what’s in a name? HindIII cuts DNA every 4096 bp (in theory)
Alul cuts DNA every 256 bp (in theory)
, Creating a recombinant DNA molecule • Types: plasmids, phages, cosmids, shuttles, BACs and
Restriction site Restriction site YACs
DNA from DNA form
source 1 source 2
Sticky end after
digestion with EcoRI
Sticky end after
digestion with EcoRI
Hydrogen bonds are
formed but there are
nicks in the backbone
“Famous plasmids”
Ligase restores F plasmid in E. coli (fertility/conjugation)
phosphodiester bonds R plasmids carrying antibiotic resistance genes
Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens (used in plant genetic engineering
Plasmids
Vectors Small, extrachromosomal DNA molecules within a cell (e.g.
Another important tool in recombinant DNA bacterium) that are physically separated from chromosomal
DNA and can replicate independently. The cell’s machinery
• ” Vehicle” to get DNA into host cell (transformation)
expresses the plasmid’s genes
• Prerequisites:
- Must be able to replicate autonomously (ori+) – DNA • Natural, self-replicating, extra-chromosomal
replication site • Small circular DNA molecule that functions independently
- Contain various unique RE sites from the host cell (autonomous replication)
- Selectable marker (AbR) -antibiotic resistance • Modified to contain an MCS/polylinker
- Should be easy to recover from host cell • Contains AbR selectable marker gene – for distinguishing
between cells that have taken up the vector
, • High copy number (+/- 1000) Insertional inactivation
• Proper MCS in lac Z (insertional inactivation) – inactivates
LacZ
• +/- 20 kb inserts
Modified to contain an MCS/polylinker
Contains AbR
selectable marker
gene
Typical DNA cloning plasmid Proper MCS in lac Z (insertional
inactivation)
Cloning in bacterial cells Blue/white selection
• ß-galactosidase catalyzes the conversion of the X-GAL
substrate to form a bright blue precipitate
• No insertion means the ß-galactosidase enzyme is
Plasmid it cut
functional, thus a blue precipitate forms
with RE Source DNA to be cloned is cut
• Insertion of a cloned DNA fragment disrupt the lac Z ORF,
with the same RE
thus ß-galactosidase is inactivated, and no blue color
visible
Ligation produces recombinant plasmid
Blue colonies – functional LacZ – non-recombinant plasmid
Transformation of bacterial White colonies – non-functional LacZ – recombinant plasmid
cells (electroporation or
calcium + heat shock)
Selection of transformed bacterial cells by antibiotic / X-gal