طالب
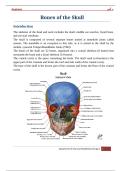
Bones of the Skull
Introduction
The skeleton of the head and neck includes the skull, middle ear ossicles, hyoid bone,
and cervical vertebrae.
The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called
sutures. The mandible is an exception to this rule, as it is united to the skull by the
mobile, synovial TemproMandibular Joints (TMJ).
The bones of the skull are 22 bones, organized into a cranial skeleton (8 bones) that
surrounds the brain and a facial skeleton (14 bones).
The cranial cavity is the space containing the brain. The skull vault (calvarium) is the
upper part of the cranium and forms the roof and side walls of the cranial cavity.
The base of the skull is the lowest part of the cranium and forms the floor of the cranial
cavity.
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1
,Anatomy أثير.د
طالب
The relatively flat bones of the vault (frontal, parietals, and part of the occipital) are
composed of external and internal tables of compact bone separated by a layer of
spongy bone called the diploë.
The cranium consist of the following bones:-
o Frontal bone: one bone
o Ethmoid bone: one bone
o Sphenoid bone: one bone
o Occipital bone: one bone
o Parietal bones: paired (2 bones)
o Temporal bones: paired (2 bones)
The facial skeleton consists of the following bones:
Zygomatic bones: paired (2 bones)
Maxillae: paired (2 bones)
Nasal bones: paired (2 bones)
Lacrimal bones: paired (2 bones)
Palatine bones: paired (2 bones)
Inferior conchae: paired (2 bones)
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2
, Anatomy أثير.د
طالب
Mandible: one bone
Vomer: one bone
The Cranial Bones:-
1- Frontal Bone
The frontal bone is a single cranial bone that forms the anterior portion of the calvaria
and upper third of the face (forehead). The frontal bone articulates laterally with the
zygoma at the frontozygomatic suture and medially with the (maxilla at the
frontomaxillary suture and nasal bones at the frontonasal sutures). In the Base of the
skull; inferiorly and deeply in anterior cranial fossa; it articulates with the ethmoid,
posteriorly; it articulates with the wings of the sphenoid bone. In the vault; it articulates
with the parietal bones at coronal suture.
The frontal bone forms a great portion of the roof of the orbit. The thickening of the
frontal bone in the anterior region forms the superciliary arches (supraorbital ridges).
These curved elevations give the prominence of eye brow region. The supraorbital
notch or foramen crosses this rim and transmits the frontal vessels and nerves (supra
orbital and supra trochlear nerves).
The frontal bone contains the frontal air sinuses (paranasal sinus), which are two hollow
spaces lined with mucous membrane, they just above the orbital margins. The paranasal
sinuses are mucous membrane lined air filled bone cavities, they are four in number:
Maxillary (the largest), Frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid paranasal sinuses, they
communicate with the nose and serve to lighten the facial skeleton and act as voice
resonators.
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 3