Theme F – photosynthesis
A study of photosynthesis in various plants and phototropic
organisms with the emphasis on the mechanisms employed by
the light dependent reactions to produce energy for use in
carbohydrate synthesis
Lecture F1 – basic processes of photosynthesis, the
chloroplast, introduction to the light reactions (pg. 513 – 521)
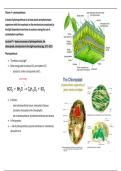
Photosynthesis
• “Synthesis using light”
• Solar energy used to reduce CO2 and oxidize H2O
- products: carbon compounds and O2
• In Plants:
- main photosynthetic tissue: mesophyll of leaves
(contains chloroplast with chlorophylls)
- site of photosynthesis: thylakoid membrane and stroma
• In Prokaryotes:
• - site of photosynthesis: plasma membrane or membranes
derived from it
, The carbon cycle in nature
Relationship of photosynthesis to other pathways
Photosynthetic vs carbohydrate metabolism
Oxidative metabolism: oxidation of carbohydrates
Reductive metabolism: production of carbohydrates
(Photosynthesis)
, General photosynthetic reaction Dark reactions:
• use ATP & NADPH to fix CO2
• do not directly require sunlight
• [CH2O] = general carbohydrate, hexose not primary product
• H2O = reducing agent
• Oxygen atoms in CO2 end up in carbohydrate
General concepts for understanding photosynthesis
Subprocesses of photosynthesis
1. Light has characteristics of both a wave and a particle
Light reactions: 2. When molecules absorb or emit light, they change their
electronic state
• Use energy from sunlight to oxidize H2O to O2
3. Photosynthetic pigments absorb the light that powers
• Produces NADPH & ATP photosynthesis
A study of photosynthesis in various plants and phototropic
organisms with the emphasis on the mechanisms employed by
the light dependent reactions to produce energy for use in
carbohydrate synthesis
Lecture F1 – basic processes of photosynthesis, the
chloroplast, introduction to the light reactions (pg. 513 – 521)
Photosynthesis
• “Synthesis using light”
• Solar energy used to reduce CO2 and oxidize H2O
- products: carbon compounds and O2
• In Plants:
- main photosynthetic tissue: mesophyll of leaves
(contains chloroplast with chlorophylls)
- site of photosynthesis: thylakoid membrane and stroma
• In Prokaryotes:
• - site of photosynthesis: plasma membrane or membranes
derived from it
, The carbon cycle in nature
Relationship of photosynthesis to other pathways
Photosynthetic vs carbohydrate metabolism
Oxidative metabolism: oxidation of carbohydrates
Reductive metabolism: production of carbohydrates
(Photosynthesis)
, General photosynthetic reaction Dark reactions:
• use ATP & NADPH to fix CO2
• do not directly require sunlight
• [CH2O] = general carbohydrate, hexose not primary product
• H2O = reducing agent
• Oxygen atoms in CO2 end up in carbohydrate
General concepts for understanding photosynthesis
Subprocesses of photosynthesis
1. Light has characteristics of both a wave and a particle
Light reactions: 2. When molecules absorb or emit light, they change their
electronic state
• Use energy from sunlight to oxidize H2O to O2
3. Photosynthetic pigments absorb the light that powers
• Produces NADPH & ATP photosynthesis