ALC Exam
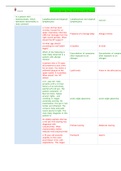
What is the difference between a statistic and a parameter? - Answer-Parameter describes the
population and statistic describes the sample
What is the sampling distribution of a statistic? - Answer-the distribution of values taken by the statistic
in all possible samples of the same size from the same population
What does it mean for an estimator to be unbiased? - Answer-An unbiased estimator is an accurate
statistic that's used to approximate a population parameter.
standard error of estimate - Answer-a measure of variability around the regression line - its standard
deviation
How do we interpret a confidence interval? - Answer-We say that a C% confidence interval means that C
% of all samples will capture the true value. That means that we are C% confident that the interval
includes the true value.
What happens to the interval as the confidence level or the sample size increases? - Answer-Higher the
confidence interval, wider the interval. As the sample size increases, the interval gets smaller.
null hypothesis - Answer-the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified
populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
Type I error (alpha) - Answer-False positive results
What is the difference between a statistic and a parameter? - Answer-Parameter describes the
population and statistic describes the sample
What is the sampling distribution of a statistic? - Answer-the distribution of values taken by the statistic
in all possible samples of the same size from the same population
What does it mean for an estimator to be unbiased? - Answer-An unbiased estimator is an accurate
statistic that's used to approximate a population parameter.
standard error of estimate - Answer-a measure of variability around the regression line - its standard
deviation
How do we interpret a confidence interval? - Answer-We say that a C% confidence interval means that C
% of all samples will capture the true value. That means that we are C% confident that the interval
includes the true value.
What happens to the interval as the confidence level or the sample size increases? - Answer-Higher the
confidence interval, wider the interval. As the sample size increases, the interval gets smaller.
null hypothesis - Answer-the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified
populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
Type I error (alpha) - Answer-False positive results