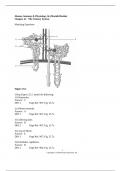
NUR2571 Professional Nursing II PN 2 Exam
2 Study Guide Questions With Correct
Answers
Cognition: - ANSWER-The mental act or process by which knowledge is acquired,
including perception, intuition, and reasoning.
Cognitive processes: - ANSWER-Needed to internalize language rules and vocabulary
in L2:
- memorization;
- categorization; and
- generalization [categorize and generalize vocabulary].
Metacognition: - ANSWER-An educational process that incorporates knowledge about
one's abilities; the demands of given tasks, and potentially effective learning strategies;
it involves self-regulation via planning, predicting, monitoring, regulating, evaluating, and
revising strategies.
Interlanguage: - ANSWER-The type of language produced by a non-native speaker in
the process of learning a second language or foreign language.
Interlanguage development: - ANSWER-The emerging language system the person
creates based on L1 and L2 knowledge to communicate in L2.
Fossilization: - ANSWER-A persistent lack of change in interlanguage patterns, even
after extended exposure to or instruction in the target language.
Acculturation: - ANSWER-Adapting to a new culture, which includes understanding
cultural expectations, semiotics, values, and beliefs is essential to second language
acquisition in that it provides appropriate context. Acculturation permits ELLs to adapt to
new cultural expectations without the loss of the culture of origin. Success with BICS
and CALP in L2 is dependent on a degree of success in L1.
Piaget Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-The Cognitive model. Children think
before they speak; speaking just reflects this thinking; language is a way for children to
represent their world.
Vygotsky Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Language is a result of
interpersonal communication.
Zone of proximal development [Vygotsky]: - ANSWER-Describes the difference
between what a person knows and what he could know if he received a personal
assistance.
, Scaffolding: - ANSWER-The process of giving temporary aid to facilitate learning.
Modeling, providing cues and encouraging.
Bronfenbrenner: - ANSWER-Created the ecological model.
B.F. Skinner: - ANSWER-Language is learned as a direct response to stimuli.
Behaviorism [Skinner]: - ANSWER-All learning whether verbal or non-verbal takes place
through the establishment of habits. Correct responses to stimuli are reinforced.
Krashen Second Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Requires natural
interactions [not grammar drills]. Students will pick up grammar rules naturally by being
immersed in L2; they need to interact with language without worrying about being
corrected. Information is given slightly above the child's level.
Pinker Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-We are predisposed to learn
language; language is a human instinct. Pinker was a disciple of Chomsky.
Chomsky Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Children are born with a knowledge
of the principles of the grammatical structure of all languages, and this inborn
knowledge explains the success and speed with which they learn language. Chomsky
created the "Universal Language". The brain has a "language acquisition device". The
Nativist model.
Stages of Language Acquisition in L1: - ANSWER-Needs interaction [nativist vs.
nurture].
Stages of Language Acquisition in L2: - ANSWER-Silence, nonverbal, understands
more than can produce; early speech production to speech emergence to intermediate
fluency.
Role of 1st language on 2nd language: - ANSWER-More academic understanding you
have in L1, more you can apply to L2;
Factors that affect L2 acquisition: - ANSWER-Age, motivation / attitude towards L2,
learning style, environmental factors, personality, status of L1, and culture in L2.
PEPSI: Stages of Language Development: - ANSWER-Level I - Pre-production stage
[Silent period]: lasts 6 months; know 500 words; minimal comprehension; no verbal
production.
Level II - Early production stage: limited comprehension; one/two-word response.
Level III - Speech emergence stage: increased comprehension; simple sentences;
some errors in speech.
Level IV - Intermediate fluency stage: very good comprehension; more complex
sentences; complex errors in speech.
2 Study Guide Questions With Correct
Answers
Cognition: - ANSWER-The mental act or process by which knowledge is acquired,
including perception, intuition, and reasoning.
Cognitive processes: - ANSWER-Needed to internalize language rules and vocabulary
in L2:
- memorization;
- categorization; and
- generalization [categorize and generalize vocabulary].
Metacognition: - ANSWER-An educational process that incorporates knowledge about
one's abilities; the demands of given tasks, and potentially effective learning strategies;
it involves self-regulation via planning, predicting, monitoring, regulating, evaluating, and
revising strategies.
Interlanguage: - ANSWER-The type of language produced by a non-native speaker in
the process of learning a second language or foreign language.
Interlanguage development: - ANSWER-The emerging language system the person
creates based on L1 and L2 knowledge to communicate in L2.
Fossilization: - ANSWER-A persistent lack of change in interlanguage patterns, even
after extended exposure to or instruction in the target language.
Acculturation: - ANSWER-Adapting to a new culture, which includes understanding
cultural expectations, semiotics, values, and beliefs is essential to second language
acquisition in that it provides appropriate context. Acculturation permits ELLs to adapt to
new cultural expectations without the loss of the culture of origin. Success with BICS
and CALP in L2 is dependent on a degree of success in L1.
Piaget Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-The Cognitive model. Children think
before they speak; speaking just reflects this thinking; language is a way for children to
represent their world.
Vygotsky Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Language is a result of
interpersonal communication.
Zone of proximal development [Vygotsky]: - ANSWER-Describes the difference
between what a person knows and what he could know if he received a personal
assistance.
, Scaffolding: - ANSWER-The process of giving temporary aid to facilitate learning.
Modeling, providing cues and encouraging.
Bronfenbrenner: - ANSWER-Created the ecological model.
B.F. Skinner: - ANSWER-Language is learned as a direct response to stimuli.
Behaviorism [Skinner]: - ANSWER-All learning whether verbal or non-verbal takes place
through the establishment of habits. Correct responses to stimuli are reinforced.
Krashen Second Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Requires natural
interactions [not grammar drills]. Students will pick up grammar rules naturally by being
immersed in L2; they need to interact with language without worrying about being
corrected. Information is given slightly above the child's level.
Pinker Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-We are predisposed to learn
language; language is a human instinct. Pinker was a disciple of Chomsky.
Chomsky Language Acquisition Theory: - ANSWER-Children are born with a knowledge
of the principles of the grammatical structure of all languages, and this inborn
knowledge explains the success and speed with which they learn language. Chomsky
created the "Universal Language". The brain has a "language acquisition device". The
Nativist model.
Stages of Language Acquisition in L1: - ANSWER-Needs interaction [nativist vs.
nurture].
Stages of Language Acquisition in L2: - ANSWER-Silence, nonverbal, understands
more than can produce; early speech production to speech emergence to intermediate
fluency.
Role of 1st language on 2nd language: - ANSWER-More academic understanding you
have in L1, more you can apply to L2;
Factors that affect L2 acquisition: - ANSWER-Age, motivation / attitude towards L2,
learning style, environmental factors, personality, status of L1, and culture in L2.
PEPSI: Stages of Language Development: - ANSWER-Level I - Pre-production stage
[Silent period]: lasts 6 months; know 500 words; minimal comprehension; no verbal
production.
Level II - Early production stage: limited comprehension; one/two-word response.
Level III - Speech emergence stage: increased comprehension; simple sentences;
some errors in speech.
Level IV - Intermediate fluency stage: very good comprehension; more complex
sentences; complex errors in speech.