1. Furosemide A 58-year-old man ran out of his congestive heart failure medications. He presents
with significant dyspnea and altered mental status. Examination reveals bibasilar
crackles and jugular venous distension. An electrocardiogram shows sinus rhythm
with low voltage complexes. Which of the following is most appropriate at this
time?
A. Amiodarone
B. Disopyramide
C. Furosemide
D. Ventricular assist device
2. Pericarditis A 15-year-old young man presents with sharp substernal chest pain that is
relieved by sitting up and leaning forward. Cardiac auscultation is normal. What
is his chest pain most likely due to?
A. Coronary ischemia
B. Costochondritis
C. Esophageal spasm
D. Pericarditis
3. Pericarditis A 55-year-old man is being evaluated for sudden onset of chest pain. He describes
the pain as sharp that is improved by sitting up and leaning forward. The chest
pain is made worse by inspiration or coughing. An ECG shows new widespread ST
segment elevation. Auscultation over the left sternal border reveals a superficial
scratchy sound. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Aortic stenosis
B. Mitral stenosis
C. Patent ductus arteriosus
D. Pericarditis
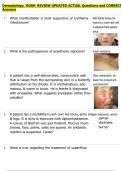
4. Atropine A 50-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department following a synco-
pal episode. On physical exam she is diaphoretic, but alert and orientated. Her
blood pressure is 100/50 mm Hg, heart rate 46 beats per minute, and respirations
12 per minute. Her rhythm strip is shown above. What is the most appropriate
, treatment for this patient's condition?
A. Adenosine
B. Amiodarone
C. Amlodipine
D. Atropine
5. Tricuspid A 40-year-old woman, who actively uses intravenous drugs, presents to the ED
with fever and fatigue for the past 3 days. In the ED, her vital signs are BP 126/82,
HR 90, RR 16, oxygen saturation 99% on room air, and temperature 101.6°F.
On exam, a murmur is noted. A transesophageal echocardiography is ordered
for suspected endocarditis. Which of the following valves is most likely to be
affected?
A. Aortic
B. Mitral
C. Pulmonic
D. Tricuspid
6. Administer clopi- A 65-year-old man presents to the ED for chest pain. You are concerned for acute
dogrel coronary syndrome and want to administer aspirin, but the patient states that he
develops angioedema to aspirin. Which of the following is the most appropriate
next step in management?
A. Administer clopidogrel
B. Administer dipyridamole
C. Administer the lower dose, 81 mg of aspirin and observe closely for angioede-
ma
D. Pretreat with corticosteroids and antihistamines and administer full-dose as-
pirin
7. Bisoprolol A 60-year-old man presents with nighttime dyspnea. His medical history is sig-
nificant for chronic hypertension. A recent echocardiogram showed an increase
in left ventricular chamber volume but normal ventricular wall thickness. Based
on this finding alone, which of the following medications is the most appropriate
, treatment for this patient's dyspnea?
A. Bisoprolol
B. Propranolol
C. Salmeterol
D. Timolol
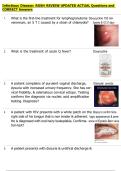
8. Chest compres- A 35-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department after being the
sions restrained driver in a motor vehicle collision. At presentation, the patient is alert,
anxious, and able to verbalize a complaint of chest pain associated with some
anterior chest wall bruising. There are no gross deformities on exam. Suddenly,
the patient becomes unresponsive. Telemetry shows the rhythm above. No pulse
can be palpated. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the
management of this patient?
A. Amiodarone drip
B. Chest compressions
C. Epinephrine
D. Synchronized cardioversion
9. Ischemic heart Which of the following is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest and
disease sudden cardiac death?
A. Anomalous coronary artery
B. Cardiomyopathy
C. Ischemic heart disease
D. Left ventricular hypertrophy
10. Ejection fraction Which of the following will help to classify heart failure as being systolic or
diastolic?
, A. Afterload
B. Ejection fraction
C. Heart rate
D. Preload
11. Beta-type natri- A 58-year-old woman presents with progressive orthopnea and peripheral ede-
uretic peptide ma. She also gets "winded" when she climbs a full flight of stairs. Which of the
following laboratory tests helps define a cardiac versus a pulmonary cause of
dyspnea?
A. Beta-2 microglobulin
B. Beta-type natriuretic peptide
C. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
D. Homovanillic acid
12. Nitroglycerin A woman complains of her heart racing, facial flushing and headache after taking
an unknown pill in her purse. Which of the following is the most likely medication?
A. Amitriptyline
B. Metformin
C. Metoprolol
D. Nitroglycerin
13. Chest pain in the Which of the following is most characteristic of Prinzmetal angina?
early morning A. Chest pain associated with nausea
B. Chest pain in the early morning
C. Exertional chest pain
D. Sub-sternal chest pain
14. Myocarditis A four-year-old girl is brought to the ED by her parents due to lethargy. A week
prior, the girl had a cough and cold. Later, symptoms progressed to include fever
and malaise. She has been less active with decreased appetite. A few hours prior
to arrival in the ER, she was having diflculty breathing. On exam, temperature
is 38.3°C, respiratory rate is 35, heart rate is 126, blood pressure is 90/60, with
clear breath sounds, hepatomegaly, and poor pulses. Which of the following is