Answers
1. junction between the shoulder
the trunk and up-
per limb
2. pectoral girdle bones connecting axial and upper appendicular skeleton (clavicle and scapula)
3. pectoral region anterior shoulder
- Overlaps with discussion of anterior thoracic wall (discussed in unit 3)
- Composed of bone, muscle, fascial planes
- Muscles collectively classified as anterior axioappendicular
4. deltoid region lateral shoulder
5. scapular region posterior shoulder
- made of bone and dense musculature
6. posterior axioap- trapezius, latissimus dorsi, levator scapulae, rhomboids
pendicular mus-
cles
7. scapulohumeral deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major, subscapularis
(intrinsic
, shoulder)
muscles
8. axioappendicu- thorax
lar muscles
origin
9. axioappendicu- scapula ,clavicle, humerus
lar muscles
attachment
10. scapulohumeral scapula
muscles origin
11. scapulohumeral humerus
muscles
attachment
12. What is the pectoral region - anterior
shoulder subdi- deltoid region - lateral
vided into? scapular region - posterior
13. Form fits func- - Almost all movements of the upper limb involve positioning the hand for manual
tion activities
- Structure emphasizes range of motion
- Stability is compromised, leading to wide variety of common injuries
14. clavicle superior margin of pectoral region
- gives degree of protection to vital neurovascular structures beneath
, "S" shaped bone that articulates with sternum medially and anteriorly and with
scapula laterally and posteriorly
- Triangular shaped sternal head articulates with manubrium, forming the stern-
oclavicular joint
- Broad, flat lateral end articulates with acromion process of scapula through
acromioclavicular joint
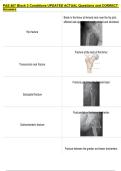
15. clavicular frac- - structural weak point 2/3 along the mid shaft of the clavicle.
tures arguably the most commonly broken bone in the body.
- fracture causes prominent deformity due to elevation of medial fragment (due
to muscle pull) and sag of lateral aspect (due to limb sag)
16. shoulder separa- separation of the acromion process from the clavicle as a result of ligament tear-
tion ing; not to be confused with shoulder dislocation; varying degrees, depending
on severity; results in point tenderness; visible upon X-ray
17.