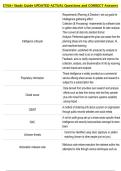
Requirements (Planning & Direction) -set out goals for
intelligence gathering effort
Collection (& Processing) -implemented by software tools
to gather data which is then processed for later analysis.
Then convert all data into standard format
Analysis- Performed against the given use cases from the
Intelligence Lifecycle planning phase and may utilize automated analysis, AI,
and machine learning
Dissemination- published info produced by analysts to
consumers who need to act on insights developed
Feedback- aims to clarify requirements and improve the
collection, analysis, and dissemination of info by receiving
correct inputs and outputs
Threat intelligence is widely provided as a commercial
Proprietary information service offering where access to updates and research is
subject to a subscription fee
Data derived from providers own research and analysis
efforts such as data from honey nets that they operate
Closed source
plus info mined from its customers systems suitability
anonymized
A method of obtaining info about a person or organization
OSINT
through public records websites and social media
A not for profit group set up to share sector specific threat
ISAC intelligence and security best practices amongst its mem-
bers
Cannot be identified using basic signature or pattern
Unknown threats
matching (known to other people just not you)
Malicious code whose execution the malware author has
obfuscation malware code
attempted to hide through various techniques such as
, compression, encryption, or encoding to severely limit
attempts to strategically analyze the malware author
Refers to the process of combining and modifying parts of
Recycled threats existing exploit code to create new threats that are not as
easily identified by automated scanning
A classification of malware that contains obfuscation tech-
Known unknowns niques to circumvent signature matching and detection
(behavior based analysis, can't predict)
Focused on hacking and computer fraud to achieve finan-
Organized crime
cial gains
Politically motivated hacker who targets governments or
Hactivist
individuals to advance their political ideologist
Group of attackers with exceptional capabilities, funding,
and organization with an intent to hack a network or sys-
Nation state
tem.
Almost all are APT
Malicious software applications that are widely available
Commodity Malware
for sale or easily obtainable and useable
Any infrastructure of hosts and services with which attack-
Command and Control (C2)
ers direct, distribute, and control malware over botnets
Blacklists if known threat sources such as malware signa-
Reputation data
tures, IP address ranges and DNS domains
A residual sign that an asset or network has been success-
Indicator of Compromise (IOC)
fully attacked or is currently under attack
Indicator of Attack (IoA) Term used for evidence of an ongoing intrusion attempt
Behavioral threat research Refers to the correlation of IoC's into attack patterns
TTP
2/8