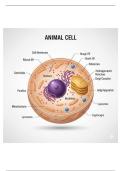
The cell membrane is a partially permeable
barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the
Describe the function of the cell membrane. movement of substances in and out to
maintain internal conditions, playing a key
role in homeostasis and cell communication.
Plant cells contain a cell wall for structural
Identify structures found in plant cells that support, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and
are absent in animal cells. a large central vacuole for storage and turgor
pressure, which are not found in animal cells.
, Mitochondria are the site of aerobic
respiration, where glucose is broken down in
Explain the role of mitochondria in cells. the presence of oxygen to release energy in
the form of ATP, often referred to as the
powerhouse of the cell.
Ribosomes are responsible for protein
synthesis, translating genetic instructions
Define the function of ribosomes.
from mRNA into polypeptides that fold into
functional proteins.
, The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance where
metabolic reactions occur, containing
Describe what occurs in the cytoplasm.
enzymes, organelles, and dissolved nutrients
that support the cell’s biochemical processes.
The nucleus contains DNA organized into
chromosomes, controlling gene expression,
Explain the role of the nucleus in a cell.
regulating cell division, and directing all
cellular activities.
barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the
Describe the function of the cell membrane. movement of substances in and out to
maintain internal conditions, playing a key
role in homeostasis and cell communication.
Plant cells contain a cell wall for structural
Identify structures found in plant cells that support, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and
are absent in animal cells. a large central vacuole for storage and turgor
pressure, which are not found in animal cells.
, Mitochondria are the site of aerobic
respiration, where glucose is broken down in
Explain the role of mitochondria in cells. the presence of oxygen to release energy in
the form of ATP, often referred to as the
powerhouse of the cell.
Ribosomes are responsible for protein
synthesis, translating genetic instructions
Define the function of ribosomes.
from mRNA into polypeptides that fold into
functional proteins.
, The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance where
metabolic reactions occur, containing
Describe what occurs in the cytoplasm.
enzymes, organelles, and dissolved nutrients
that support the cell’s biochemical processes.
The nucleus contains DNA organized into
chromosomes, controlling gene expression,
Explain the role of the nucleus in a cell.
regulating cell division, and directing all
cellular activities.