Polymers
Polymer – a large molecule made from joining together many shorter molecules
Monomer – a small molecule that can join to other molecules to form a polymer
Addition Polymers
Long chain molecules made from joining together many shorter molecules (monomers) to form
a long chain molecule with nothing else produced
Monomers – alkenes, molecules with C=C bonds
Examples – poly(ethene), PVC, poly(propene)
Non-biodegradable due to the absence of polar bonds in the main chain (all bonds are C–C)
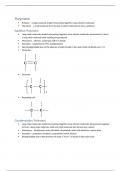
Monomer
Structure
Repeating unit
Condensation Polymers
Long chain molecules made from joining together many shorter molecules (monomers) together
to form a long chain molecule, with one small molecule also formed (e.g. water)
Monomers – dicarboxylic acids with diols, dicarboxylic acids with diamines, amino acids
Examples – polyesters (terylene), polyamides (nylon, Kevlar)
Biodegradable due to the presence of polar C–N or C–O bonds in the main chain
Polymer – a large molecule made from joining together many shorter molecules
Monomer – a small molecule that can join to other molecules to form a polymer
Addition Polymers
Long chain molecules made from joining together many shorter molecules (monomers) to form
a long chain molecule with nothing else produced
Monomers – alkenes, molecules with C=C bonds
Examples – poly(ethene), PVC, poly(propene)
Non-biodegradable due to the absence of polar bonds in the main chain (all bonds are C–C)
Monomer
Structure
Repeating unit
Condensation Polymers
Long chain molecules made from joining together many shorter molecules (monomers) together
to form a long chain molecule, with one small molecule also formed (e.g. water)
Monomers – dicarboxylic acids with diols, dicarboxylic acids with diamines, amino acids
Examples – polyesters (terylene), polyamides (nylon, Kevlar)
Biodegradable due to the presence of polar C–N or C–O bonds in the main chain