Complete Solutions
4 Classes of Signal Transduction Correct Answers 1.) ligand-
gated ion channels (nACh, AMPA/KA, NMDA)
2.) G protein-coupled receptors (mACh, DA, NE, 5-HT,
GABAb, peptides)
3.) Enzymes-linked receptors (NGF/BDNF receptor)
4.) Intracellular (cytosolic) receptors (steroid hormone
receptors)
Absolute Refractory Period Correct Answers ○first stage of
the refractory period where it is impossible to initiate another
action potential
○prevents the backwards movement of APs and limit the rate of
firing
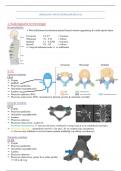
Acetylcholine (ACh) Correct Answers *Functions:*
○PNS: affects muscle movement
○CNS: reduces stress, cortical arousal (ex. nicotine)
*Locations:*
○CNS: basal forebrain, tegmentum
○PNS: NMJ, ANS
*Synthesis:*
○one step
○Choline + acetyl CoA
○ChAT
*Inactivation:*
○one step
○AChE (insecticides, Sarin, VX, caffeine)
*Receptors:*
,○(i) nAChR
○(m) mAChR
ACh Disorders Correct Answers can cause:
○bradycardia
○hypotension
○hypersecretion
○prolonged muscle contractions
ACh Receptors (nAChR) Correct Answers ○ionotropic
receptors
○ACh binds and opens a pore that conducts both Na+ and K+
○composed of multiple 5-protein subunits (heteropentameric)
ACh Treatment Uses Correct Answers can treat:
○glaucoma
○neuropsychiatric symptoms
○prolonged REM sleep
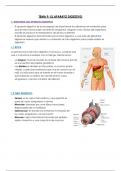
Actin Correct Answers ○acts like a rope to move vesicles long
distances
○involved in trafficking and endocytosis
Action Potentials (APs) Correct Answers ○non-decremental
because they use ATP to activate
○ conducted slower than PSPs
○passive and active (uses ATP)
○a new AP is actively generated at each Node of Ranvier
○moves like a wave down the axon from node to node
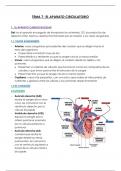
, Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) Correct Answers ○catalyzes the
conversion of ATP to cAMP
○Gs stimulates AC to promote formation of cAMP
Gi/Go inhibits AC to reduce cAMP levels
Agonist Correct Answers ○increases or facilitates activity
○mimics NTs
○blocks autoreceptors or reuptake
○increases synthesis of NTs
Antagonist Correct Answers ○decreases or inhibits activity
○blocks synthesis of NTs
○blocks release of NTs
○blocks receptor binding
ASsociativity Correct Answers transmission at one synapse
can increase the strength of transmission at another synapse that
is active at the same time
Axo-Axonic Synapse Correct Answers ○3 neurons where the
3rd neuron modulates the other two
○axon terminal of one neuron synapses on the axon terminal of
another
○function either facilitates or inhibits the NT release
○can release more or less NT
Axo-Dendritic Synapse Correct Answers ○most common
synapse type
○one receiving and one sending neuron