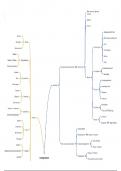
Section 9 - Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chapter 20 - The Electron-Transport Chain
● Oxidative phosphorylation
○ Redox reactions that allow the flow of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to
oxygen
■ Exergonic
○ 4 large protein complexed embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
■ Respiratory chain or electron-transport chain
■ 3 complexed → use the energy released by the electron flow to pump
protons from the mitochondrial matrix into the space between the
inner and outer mitochondrial membranes
■ Proton gradient → used to power the synthesis of ATP by oxidative
phosphorylation
● (Cellular) respiration: the generation of high-transfer-potential electrons by the citric
acid cycle, their flow through the respiratory chain, and the accompanying synthesis
of ATP
20.1 - Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eukaryotes Takes Place in
Mitochondria
● Mitochondria are bounded by a double membrane
○ Outer membrane
■ Permeable to most small molecules and ions → it contains many
copies of mitochondrial porin (VDAC, Voltage-Dependent Anion
Channel)
● Regulates the flux of molecules crucial to the function of
cellular respiration across the outer membrane
○ Extensive, highly folded inner membrane
■ Folded into a series of internal ridges → cristae
■ Site of oxidative phosphorylation
■ Impermeable to nearly all ions and polar
molecules
■ 2 faces → matrix site and the cytoplasmic side
○ 2 compartments
■ Intermembrane space: space between the outer and inner
membranes
■ Matrix → bounded by the inner membrane
● Site of reactions of the citric acid cycle and fatty oxidation
, 20.2 - Oxidative Phosphorylation Depends on Electron Transfer
● 4 protein complexes
○ increasing redox potential
20.3 - The Respiratory Chain Consists of Proton Pumps and a Physical
Link to the Citric Acid Cycle
● Electrons are transferred from NADH to O2 through a
chain of 4 protein complexes
○ Electron flow within 3 of these transmembrane
complexes leads to the transport of protons
across the inner mitochondrial membrane
■ NADH-Q oxidoreductase
■ Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
■ Cytochrome c oxidase
○ The 4th protein complex does not pump protons
■ Succinate-Q reductase
● The high-potential electrons of NADH enter the
respiratory chain at NADH-Q oxidoreductase/Complex I/
NADH dehydrogenase)
○ Enzyme consisting of 45 polypeptide chains
organized into 14 core subunits
■ 2 types of prosthetic groups
● FMN and iron-sulfur clusters
○ L-shaped
■ Hydrophobic horizontal arm lying in the membrane
■ Hydrophilic vertical arm projecting into the matrix
Chapter 20 - The Electron-Transport Chain
● Oxidative phosphorylation
○ Redox reactions that allow the flow of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to
oxygen
■ Exergonic
○ 4 large protein complexed embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
■ Respiratory chain or electron-transport chain
■ 3 complexed → use the energy released by the electron flow to pump
protons from the mitochondrial matrix into the space between the
inner and outer mitochondrial membranes
■ Proton gradient → used to power the synthesis of ATP by oxidative
phosphorylation
● (Cellular) respiration: the generation of high-transfer-potential electrons by the citric
acid cycle, their flow through the respiratory chain, and the accompanying synthesis
of ATP
20.1 - Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eukaryotes Takes Place in
Mitochondria
● Mitochondria are bounded by a double membrane
○ Outer membrane
■ Permeable to most small molecules and ions → it contains many
copies of mitochondrial porin (VDAC, Voltage-Dependent Anion
Channel)
● Regulates the flux of molecules crucial to the function of
cellular respiration across the outer membrane
○ Extensive, highly folded inner membrane
■ Folded into a series of internal ridges → cristae
■ Site of oxidative phosphorylation
■ Impermeable to nearly all ions and polar
molecules
■ 2 faces → matrix site and the cytoplasmic side
○ 2 compartments
■ Intermembrane space: space between the outer and inner
membranes
■ Matrix → bounded by the inner membrane
● Site of reactions of the citric acid cycle and fatty oxidation
, 20.2 - Oxidative Phosphorylation Depends on Electron Transfer
● 4 protein complexes
○ increasing redox potential
20.3 - The Respiratory Chain Consists of Proton Pumps and a Physical
Link to the Citric Acid Cycle
● Electrons are transferred from NADH to O2 through a
chain of 4 protein complexes
○ Electron flow within 3 of these transmembrane
complexes leads to the transport of protons
across the inner mitochondrial membrane
■ NADH-Q oxidoreductase
■ Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
■ Cytochrome c oxidase
○ The 4th protein complex does not pump protons
■ Succinate-Q reductase
● The high-potential electrons of NADH enter the
respiratory chain at NADH-Q oxidoreductase/Complex I/
NADH dehydrogenase)
○ Enzyme consisting of 45 polypeptide chains
organized into 14 core subunits
■ 2 types of prosthetic groups
● FMN and iron-sulfur clusters
○ L-shaped
■ Hydrophobic horizontal arm lying in the membrane
■ Hydrophilic vertical arm projecting into the matrix