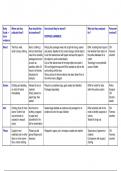
Theme Two: Building a business
Topic 2.1 Growing the business
2.1.1 Business growth
2.1.2 Changes in business aims and objectives
2.1.3 Business and globalisation
2.1.4 Ethics, the environment and business
Topic 2.2 Making marketing decisions
2.2.1 Product
2.2.2 Price
2.2.3 Promotion
2.2.4 Place
2.2.5 Using the marketing mix to make business decisions
Topic 2.3 Making operational decisions
2.3.1 Business operations
2.3.2 Working with suppliers
2.3.3 Managing quality
2.3.4 The sales process
Topic 2.4 Making financial decisions
2.4.1 Business calculations
2.4.2 Understanding business performance
Topic 2.5 Making human resource decisions
2.5.1 Organisational structures
2.5.2 Effective recruitment
2.5.3 Effective training and development
2.5.4 Motivation
,Topic 2.1 Growing the business
2.1.1 Business growth
Business growth - Expanding sales, revenue, market share and/or entering new markets
1. Growth can be internal - organic
● from within the business by (usually) reinvesting profits to expand
2. Growth can be external - inorganic
● expansion by buying other businesses or by merging with another business
Organic growth
1. New products: innovation means a business creates something new and brings it to market
- Businesses which spend more on R&D (research and development) tend to be more
successful with innovation.
- Product diversification opens new revenue streams
2. New markets: expanding overseas by selling to a new market abroad can lead to growth.
- Take advantage of the dynamic nature of technology, which would create new growth
opportunities.
- Another way to attract a ‘new market’ is to adapt the marketing mix and sell to a new
group of customers.
Advantages
- Pace of growth is manageable
- Less risky as growth is financed by profits, there is existing business expertise in the industry
- The management knows & understands every part of the business
Disadvantages
- Pace of growth can be slow and frustrating, could miss out on lucrative market opportunities
- Not necessarily able to benefit from lower unit costs (e.g. bulk purchasing discounts from
suppliers) as larger firms would be able to
- Access to finance may be limited
Inorganic growth
Merger: two businesses mutually (meaning they both agree) decide to join and operate
together.
Takeover: when a business (sometimes aggressively) purchases more than 50% of the shares of
another business.
Advantages
Economies of scale – ↓costs by bulk buying.
Cut costs by removing duplicated workers and premises.
Faster than growing organically.
Removes a rival – less competition, higher market share
More skills, ideas and experience working together – create new products and meet customer
needs better to expand into new markets
,Disadvantages
Cutting costs by sacking workers could damage the brand image and reputation of the
business.
Less competition, choice and maybe ↑prices for consumers.
Two businesses may have a ‘culture clash’ as their brands do not work well together.
Could be blocked by the CMA (government authority).
Economies of scale
- When a business becomes larger (either organic or inorganic growth), they can lower
their costs.
- Larger businesses have more bargaining power when it comes to purchasing stock from
their suppliers.
- When a large business can bulk buy products, they can negotiate a discount (↓cost)
from the supplier.
- This ability to bulk buy is an example of economies of scale and can reduce costs.
- Once costs are reduced, the business can then reduce prices.
Key terms
Innovation - Creating something new and bringing it to the market.
Inorganic growth - Growing by buying other businesses or merging.
Research and development (R&D) - Spending on research and development to innovate.
Culture Clash - When two businesses come together but are not compatible.
Takeover - One business (sometimes aggressively) buying another.
Economies of scale - One business (sometimes aggressively) buying another.
CMA - Government authority in charge of competition.
Merger - Two businesses mutually agreeing to come together.
Organic growth - Growing by reinvesting profits.
Sources of finance for a start-up or established small business:
Short-term sources: overdraft and trade credit
Long-term sources: personal savings, venture capital, share capital, loans, retained profit and
crowdfunding
Retained profit
This is profit (revenue – total costs) which has been kept back (retained) by the business.
- It has not been paid out in dividends.
- This money is good as no interest is charged and is quick to use.
When using retained profit, be careful to make sure that the business does have retained
profit.
This would not be correct if the business was completely new or has been making losses in
previous years.
Selling assets
An asset is anything a business owns, such as a building, machine or another business.
- Like retained profit in that there is no interest to pay, and the owner maintains full control.
Once the asset is sold, this can be used as finance.
, However, it depends if the business has any assets to sell and if they can find somebody to buy
the asset.
Some businesses sell their machinery and then lease (rent) it back - this increases monthly
costs.
What is sold (is it needed?) is significant.
Loan capital
Money borrowed from a bank and paid back with additional interest (increasing fixed costs).
Loans can be for 1 year or even 35 years.
They are usually paid back monthly.
Owner does not lose control of their business.
Interest rates can either be fixed (do not change) or variable.
Opportunity to evaluate - the cost of the loan depends upon whether interest is fixed/variable.
Loan - collateral and risk
Security (or collateral) is an asset used to guarantee a loan.
- If the loan is not repaid, then the bank seizes this asset.
Collateral could be a property, machinery or a factory.
- Meaning that if a business fails to pay their loan, then they could lose a key part of their
business!
New and smaller businesses find it much harder to successfully apply for a loan.
The greater the risk of failure, the higher the interest rate charged by the bank.
Share capital
Investment received in exchange for new shares being created and given in return.
The company can raise finance by issuing/creating new shares and giving them to:
- Existing owners/shareholders or
- New owners/shareholders in return for investment.
Once the investment has been made, it is the company that owns the money provided.
- No interest is charged, and the investment is not repaid back – benefits.
Creating new shares can have consequences for existing shareholders… as it could dilute the %
that they own.
- Venture capital does not involve new shares being created, but instead gives away existing
shares.
Benefits
Dividends are not paid if the business makes a loss.
Not repaid and no interest – unlike a loan.
Accompanied with advice and guidance.
Large investors also want success and so will be motivated to help the business.
Drawbacks
Arguments and disagreements could occur between the owner and investors.
Decision-making may be slower with more people involved.
The owner will lose control if they give away more than 50%.
Dividends are paid into perpetuity (forever) and do not end – unlike a loan.
Public limited company (plc)
Topic 2.1 Growing the business
2.1.1 Business growth
2.1.2 Changes in business aims and objectives
2.1.3 Business and globalisation
2.1.4 Ethics, the environment and business
Topic 2.2 Making marketing decisions
2.2.1 Product
2.2.2 Price
2.2.3 Promotion
2.2.4 Place
2.2.5 Using the marketing mix to make business decisions
Topic 2.3 Making operational decisions
2.3.1 Business operations
2.3.2 Working with suppliers
2.3.3 Managing quality
2.3.4 The sales process
Topic 2.4 Making financial decisions
2.4.1 Business calculations
2.4.2 Understanding business performance
Topic 2.5 Making human resource decisions
2.5.1 Organisational structures
2.5.2 Effective recruitment
2.5.3 Effective training and development
2.5.4 Motivation
,Topic 2.1 Growing the business
2.1.1 Business growth
Business growth - Expanding sales, revenue, market share and/or entering new markets
1. Growth can be internal - organic
● from within the business by (usually) reinvesting profits to expand
2. Growth can be external - inorganic
● expansion by buying other businesses or by merging with another business
Organic growth
1. New products: innovation means a business creates something new and brings it to market
- Businesses which spend more on R&D (research and development) tend to be more
successful with innovation.
- Product diversification opens new revenue streams
2. New markets: expanding overseas by selling to a new market abroad can lead to growth.
- Take advantage of the dynamic nature of technology, which would create new growth
opportunities.
- Another way to attract a ‘new market’ is to adapt the marketing mix and sell to a new
group of customers.
Advantages
- Pace of growth is manageable
- Less risky as growth is financed by profits, there is existing business expertise in the industry
- The management knows & understands every part of the business
Disadvantages
- Pace of growth can be slow and frustrating, could miss out on lucrative market opportunities
- Not necessarily able to benefit from lower unit costs (e.g. bulk purchasing discounts from
suppliers) as larger firms would be able to
- Access to finance may be limited
Inorganic growth
Merger: two businesses mutually (meaning they both agree) decide to join and operate
together.
Takeover: when a business (sometimes aggressively) purchases more than 50% of the shares of
another business.
Advantages
Economies of scale – ↓costs by bulk buying.
Cut costs by removing duplicated workers and premises.
Faster than growing organically.
Removes a rival – less competition, higher market share
More skills, ideas and experience working together – create new products and meet customer
needs better to expand into new markets
,Disadvantages
Cutting costs by sacking workers could damage the brand image and reputation of the
business.
Less competition, choice and maybe ↑prices for consumers.
Two businesses may have a ‘culture clash’ as their brands do not work well together.
Could be blocked by the CMA (government authority).
Economies of scale
- When a business becomes larger (either organic or inorganic growth), they can lower
their costs.
- Larger businesses have more bargaining power when it comes to purchasing stock from
their suppliers.
- When a large business can bulk buy products, they can negotiate a discount (↓cost)
from the supplier.
- This ability to bulk buy is an example of economies of scale and can reduce costs.
- Once costs are reduced, the business can then reduce prices.
Key terms
Innovation - Creating something new and bringing it to the market.
Inorganic growth - Growing by buying other businesses or merging.
Research and development (R&D) - Spending on research and development to innovate.
Culture Clash - When two businesses come together but are not compatible.
Takeover - One business (sometimes aggressively) buying another.
Economies of scale - One business (sometimes aggressively) buying another.
CMA - Government authority in charge of competition.
Merger - Two businesses mutually agreeing to come together.
Organic growth - Growing by reinvesting profits.
Sources of finance for a start-up or established small business:
Short-term sources: overdraft and trade credit
Long-term sources: personal savings, venture capital, share capital, loans, retained profit and
crowdfunding
Retained profit
This is profit (revenue – total costs) which has been kept back (retained) by the business.
- It has not been paid out in dividends.
- This money is good as no interest is charged and is quick to use.
When using retained profit, be careful to make sure that the business does have retained
profit.
This would not be correct if the business was completely new or has been making losses in
previous years.
Selling assets
An asset is anything a business owns, such as a building, machine or another business.
- Like retained profit in that there is no interest to pay, and the owner maintains full control.
Once the asset is sold, this can be used as finance.
, However, it depends if the business has any assets to sell and if they can find somebody to buy
the asset.
Some businesses sell their machinery and then lease (rent) it back - this increases monthly
costs.
What is sold (is it needed?) is significant.
Loan capital
Money borrowed from a bank and paid back with additional interest (increasing fixed costs).
Loans can be for 1 year or even 35 years.
They are usually paid back monthly.
Owner does not lose control of their business.
Interest rates can either be fixed (do not change) or variable.
Opportunity to evaluate - the cost of the loan depends upon whether interest is fixed/variable.
Loan - collateral and risk
Security (or collateral) is an asset used to guarantee a loan.
- If the loan is not repaid, then the bank seizes this asset.
Collateral could be a property, machinery or a factory.
- Meaning that if a business fails to pay their loan, then they could lose a key part of their
business!
New and smaller businesses find it much harder to successfully apply for a loan.
The greater the risk of failure, the higher the interest rate charged by the bank.
Share capital
Investment received in exchange for new shares being created and given in return.
The company can raise finance by issuing/creating new shares and giving them to:
- Existing owners/shareholders or
- New owners/shareholders in return for investment.
Once the investment has been made, it is the company that owns the money provided.
- No interest is charged, and the investment is not repaid back – benefits.
Creating new shares can have consequences for existing shareholders… as it could dilute the %
that they own.
- Venture capital does not involve new shares being created, but instead gives away existing
shares.
Benefits
Dividends are not paid if the business makes a loss.
Not repaid and no interest – unlike a loan.
Accompanied with advice and guidance.
Large investors also want success and so will be motivated to help the business.
Drawbacks
Arguments and disagreements could occur between the owner and investors.
Decision-making may be slower with more people involved.
The owner will lose control if they give away more than 50%.
Dividends are paid into perpetuity (forever) and do not end – unlike a loan.
Public limited company (plc)