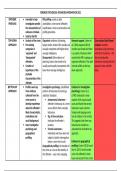
FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGY ADVANCED INFORMATION 2022
OFFENDER Intended to help FBI profiling: works on data
PROFILING investigators predict assimilation, crime scene (offender)
the characteristics of classification, crime reconstruction and
unknown criminals. profile generation.
Used by the FBI.
TOP-DOWN Analysis of the crime. Organised: evidence of planning, Research support: Canter et Cross-cultural bias/flawed
APPROACH Pre-existing targets victim, tends of the socially and al. (1004) analysed 100 US evidence: method
categories of sexually competent with higher-than- murders and found that there developed using interviews
‘organised’ and average intelligence. is a subset of features which with 36 US murderers – FBI
‘disorganised’ Disorganised: little evidence of matched the FBI’s typology of did not standardise
offenders. planning, leaves clues tends to be organised offenders. This adds interviews meaning that the
Creation of socially and sexually incompetent with internal validity to the top- approach lacks scientific
hypotheses of the lower-than-average intelligence. down approach. basis.
probable
characteristics of the
offender.
BOTTOM-UP Profilers work up Investigative psychology: established Evidence for investigative
APPROACH from evidence patterns of behaviour by forming a psychology: Canter et al.
collected from the statistical ‘database’. (1990) conducted a meta-
crime scene to Interpersonal coherence – analysis of 66 sexual assault
develop hypotheses offenders’ behaviour at a crime cases and found that several
about the offender's scene reflects their everyday behaviours were common
likely characteristics, behaviour. (impersonal language and a
motivations and Sig. of time and place – lack of relation to the victim).
social background. indicates the offender’s This suggests that there was
Uses investigative location. behavioural consistency –
psychology and Forensic awareness – advocated by the bottom-up
geographical individuals who have been the approach.
profiling. subject of police interrogation
before ‘cover their tracks’. Evidence for geographical
Geographical profiling: the location of profiling: Canter (2001) found
the crime as a clue to the identity of that in 120 US serial murder
the offender – uses crime mapping, cases, the offender’s home
base was located in the centre
OFFENDER Intended to help FBI profiling: works on data
PROFILING investigators predict assimilation, crime scene (offender)
the characteristics of classification, crime reconstruction and
unknown criminals. profile generation.
Used by the FBI.
TOP-DOWN Analysis of the crime. Organised: evidence of planning, Research support: Canter et Cross-cultural bias/flawed
APPROACH Pre-existing targets victim, tends of the socially and al. (1004) analysed 100 US evidence: method
categories of sexually competent with higher-than- murders and found that there developed using interviews
‘organised’ and average intelligence. is a subset of features which with 36 US murderers – FBI
‘disorganised’ Disorganised: little evidence of matched the FBI’s typology of did not standardise
offenders. planning, leaves clues tends to be organised offenders. This adds interviews meaning that the
Creation of socially and sexually incompetent with internal validity to the top- approach lacks scientific
hypotheses of the lower-than-average intelligence. down approach. basis.
probable
characteristics of the
offender.
BOTTOM-UP Profilers work up Investigative psychology: established Evidence for investigative
APPROACH from evidence patterns of behaviour by forming a psychology: Canter et al.
collected from the statistical ‘database’. (1990) conducted a meta-
crime scene to Interpersonal coherence – analysis of 66 sexual assault
develop hypotheses offenders’ behaviour at a crime cases and found that several
about the offender's scene reflects their everyday behaviours were common
likely characteristics, behaviour. (impersonal language and a
motivations and Sig. of time and place – lack of relation to the victim).
social background. indicates the offender’s This suggests that there was
Uses investigative location. behavioural consistency –
psychology and Forensic awareness – advocated by the bottom-up
geographical individuals who have been the approach.
profiling. subject of police interrogation
before ‘cover their tracks’. Evidence for geographical
Geographical profiling: the location of profiling: Canter (2001) found
the crime as a clue to the identity of that in 120 US serial murder
the offender – uses crime mapping, cases, the offender’s home
base was located in the centre