CHAPTER SIX
HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM AND
SENSE ORGANS
GENERAL
● Detects changes in the external environment and reacts to those changes
● Detects changes in an internal environment and reacts to them
● Helps bring about coordination
NERVOUS TISSUE
● Nerves are made of nerve fibres held together by connective tissue
● Nerve fibres are made up of neurons
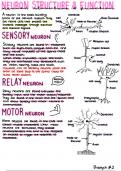
SENSORY NEURONS
● Carry impulses from receptors to the central nervous system
,MOTOR NEURONS
● Carry impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors
CONNECTOR NEURONS
● Also known as interneurons
● Carry impulses inside the central nervous system from a sensory neuron
to a motor neuron
, CELL BODY
● Contains a prominent nucleus, cytoplasm with nissl granules,
mitochondria, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
● Dendrites carry impulses towards the body
AXON
● Single long outgrowth
● Conduct impulses away from the cell body
● Has branched endings (terminal branches)
● Covered by neurilemma and myelin sheath
SYNAPSE
● The microscopic gap between the axon terminals of one neuron and the
dendrites of the next
● Communication across a synapse is by means of chemicals called
neurotransmitters
● This communication is called synaptic contact
HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM AND
SENSE ORGANS
GENERAL
● Detects changes in the external environment and reacts to those changes
● Detects changes in an internal environment and reacts to them
● Helps bring about coordination
NERVOUS TISSUE
● Nerves are made of nerve fibres held together by connective tissue
● Nerve fibres are made up of neurons
SENSORY NEURONS
● Carry impulses from receptors to the central nervous system
,MOTOR NEURONS
● Carry impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors
CONNECTOR NEURONS
● Also known as interneurons
● Carry impulses inside the central nervous system from a sensory neuron
to a motor neuron
, CELL BODY
● Contains a prominent nucleus, cytoplasm with nissl granules,
mitochondria, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
● Dendrites carry impulses towards the body
AXON
● Single long outgrowth
● Conduct impulses away from the cell body
● Has branched endings (terminal branches)
● Covered by neurilemma and myelin sheath
SYNAPSE
● The microscopic gap between the axon terminals of one neuron and the
dendrites of the next
● Communication across a synapse is by means of chemicals called
neurotransmitters
● This communication is called synaptic contact