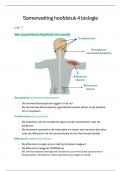
ACCURATE SOLUTIONS
1. Dementia that results from conditions that block or reduce
blood flow to the brain (HTN, diabetes, hyperlipidemia)
Vascular Dementia
Frontotemporal
Dementia Lewy Body
Dementia
Alzheimer's Disease
2. Why might a patient with Barrett's esophagus seek a
prescription from a Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) instead of
a gastroenterologist?
The patient has a new diagnosis unrelated to Barrett's
esophagus. The patient is seeking a second opinion on
their treatment.
The patient's gastroenterologist is no longer covered by
insurance.
The patient prefers the FNP's approach to treatment.
3. In a clinical scenario where a patient presents with symptoms
of acute bacterial proctatitis but has a negative urinalysis,
,what would be the next best step in diagnosis?
Repeat the urinalysis for accuracy.
Conduct a physical examination without further testing.
Perform a vigorous massage of the prostate to release
fluid for culture.
Initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics immediately.
,4. Mrs. Smith, a 75-year-old woman, is brought to the clinic by her
daughter, who expresses concerns about her mother's recent
forgetfulness and confusion. Mrs. Smith often repeats questions,
struggles to recall recent events, and has difficulty following
simple instructions. The clinician decides to assess Mrs. Smith's
cognitive function using a screening tool. What is the most
appropriate tool for this initial assessment, especially considering
her age and presenting symptoms?
Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)
Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale
(HARS) Geriatric Depression Scale
(GDS)
5. What are two potential conditions indicated by the patient's
memory and organizational difficulties?
Anxiety and Depression
Alzheimer's and Delirium
Bipolar Disorder and PTSD
Parkinson's and Schizophrenia
6. A 14-year-old wrestler reports erythematous plaques with peripheral
scaling and central clearing on his arms. The symptoms support
a diagnosis of
Tinea pedis
Tinea corporis
Tinea faciei
Tinea
, barbae