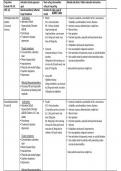
Improvement and Learning curve - Correct Answer-this model shows that as the
number of task repetitions increases, efficiency improves because of learning or
improvement. Doubling the cumulative production reduces the time to complete the
task.
Cash flow diagram - Correct Answer-used to model the positive and negative cash flow
of potential investment opportunities
First cost - Correct Answer-expense to build or buy and install
Operating and Maintenance (O&M) - Correct Answer-annual expense, such as labor,
electricity and minor repairs
Salvage value - Correct Answer-receipt at project termination for sale or transfer of the
equipment (Can be a cost)
Revenues - Correct Answer-annual receipts due to sale of products or services
Overhaul - Correct Answer-major capital expenditure that occurs during the asset's life
Typical life cycle - Correct Answer-1. needs assessment and justification (requirements)
2. Conceptual or preliminary design (impact analysis)
3. detailed design (detailed specifications)
4. production or construction
5. operational use (maintenance and support)
6. Decline and retirement (responsible disposal)
Maximize profit - Correct Answer-most common criterion in engineering decision
making. Consists of three categories: fixed input, fixed output, neither input or output
fixed.
If fixed input, - Correct Answer-maximize benefits or outputs
If fixed output, - Correct Answer-minimize costs or inputs
If neither input or output fixed, - Correct Answer-Maximum profit = Value of outputs -
Value of inputs
Types of estimates - Correct Answer-Rough
Semi-Detailed
Detailed
, Rough estimate - Correct Answer-Used for high-level planning, determining feasibility,
and initial planning and evaluation phases. Typical accuracy of -30% to 60 %
Semi-Detailed Estimate - Correct Answer-Used for budgeting purposes at the
conceptual or preliminary design stage. Typical accuracy of -15% to 20%
Detailed Estimate - Correct Answer-used during detailed design and contract bidding
phases. Typical accuracy: -3% to 5%
Relationship: Accuracy vs. Cost - Correct Answer-As Accuracy increases, cost of
estimate increases
What do engineers do? - Correct Answer-Apply science and math to solve problems
Types of problems - Correct Answer-Simple (not much time and effort)
Intermediate (economic)
Complex (mix of economic, political and humanistic elements)
Decision-making process - Correct Answer-1. recognize the problem
2. define the goal or objective
3. assemble relevant data
4. identify alternatives
5. select criterion to determine best alternative
6. construct model
7. predict outcomes
8. choose best alternative
9. audit result
Difficulties in estimation - Correct Answer-*One-of-a-kind Estimate ("close cousin"
approach)
*Time and Effort available (Everything has a price tag)
*Estimator experience("Knowledge is power")
Per-Unit and segmenting estimation model - Correct Answer-model that uses different
levels of detail, and cost and benefit per square foot
Cost index estimation model - Correct Answer-model that reflects historical change in
costs.
Cost at time A / Cost at time B = Index Value at time A / Index Value at time B
Power-sizing model - Correct Answer-model used for scaling-up or down a known cost
quantity.
Cost of equipment A/Cost of equipment B = (Size of A/Size of B)^x
** works best when size ration is between 2 and 5