Lecture 2
Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
Period 1, Week 1
Communication among neurons
Either fire or do not fire
All-or-none law
Intensity variations by
1. No of neurons firing
2. Variations in firing rate
Neurons interact
Via synapses
Through chemical substances
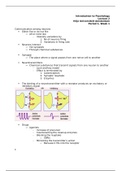
Synapse
The place where a signal passes from one nerve cell to another
Neurotransmitters
Chemical substances that transmit signals from one neuron to another
Lock-and-key model
Effect is terminated by
1. Autoreceptors
2. Synaptic reuptake
3. Enzymes
The binding of a neurotransmitter with a receptor produces an excitatory or
inhibitory signal
Drugs
Agonists
Increase of precursor
Counteracting the cleanup enzymes
Blocking the reuptake
o SSRIs
Mimicking the transmitter’s action
o Because it fits into the receptor
1
, Antagonists – antipsychotics
Decrease precursor (or neurotransmitter)
Increase effectiveness cleanup enzymes
Enhance the reuptake
Blocking of receptors
Studying the brain
19th century > Phrenology
Bumps on the skull were interpreted in terms of personality traits
Methods for studying the brain
Clinical observation of patients with brain damage
Experimental techniques
Invasive: animal studies
TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
EEG
ERP
fMRI
MRI
PET
Introduction to Psychology
Lecture 3
Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
Period 1, Week 2
Consciousness: one’s subjective experience of the world, resulting from brain
activity
Brain and mind are inseparable
Everyone experiences consciousness personally
Arises as a function of which brain circuits are active
Global Workspace Model
Sometimes unconscious processes lead people to do things that their
conscious minds struggle to explain
After-the-face explanations
Variations in consciousness
Attention: refers to the process that enables you to focus selectively on some
things and avoid focusing on others
There is a limit to the number of things you can be conscious of at the
same time
Unattended behavior may still affect behavior > subliminal perception
Yet, without much awareness > change blindness
Cocktail party phenomenon
Sometimes the unattended information breaks through
Sleep
Why do we sleep? > theories about sleep
Restorative theory
Circadian rhythm theory
2
, Facilitation of learning theory > strengthening of neural
connections and memory consolidation
Dreams: products of an altered state of consciousness in which images
and fantasies are confused with reality
Non-REM dreams: dull
REM dreams: bizarre and intense
Drugs
Addiction: drug use that remains compulsive despite its negative
consequences
Physical and psychological dependence
Tolerance: increasing amounts of a drug needed to achieve the
intended effect
Withdrawal: physiological and psychological state characterized
by feelings of anxiety, tension and cravings for the addictive
substance
Four major categories of drugs
Stimulants: drugs that increase behavioral and mental activity and activate
the sympathetic nervous system (e.g. amphetamines, methamphetamines,
cocaine, nicotine, caffeine)
Depressants: reduce behavioral and mental activity by depressing the central
nervous system (e.g. alcohol, benzo’s, barbiturates)
Opiates (narcotics): depress or slow down the central nervous system, relieve
pain and suffering (e.g. heroin, morphine, codeine)
Hallucinogens (psychedelics): produce alterations in cognition, mood and
perception (e.g. LSD, Mescaline – from Peyote cactus, psilocybin mushrooms)
Many do not fit into these four categories (XTC, MDMA, marijuana)
Introduction to Psychology
Lecture 4
Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
Period 1, Week 2
Sensation: the detection of external stimuli and the transmission of this information
to the brain
Perception: the processing, organization, and interpretation of sensory signals
Distal stimulus > proximal stimulus > transduction > sensation > perception
The senses
Vision
Hearing
Taste
Smell
Skin senses
Vestibular sense – sense of balance
Kinesthesis – sense of muscles/tendants/joints
3