Abbie Bluer
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
Postpartum Disorder
CONCEPT ______________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________ 20
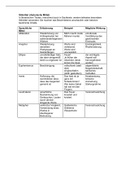
Related Content Underlying Principles Nursing Interventions
(E.G., DELEGATION, WHO? WHEN? WHY? HOW?
LEVELS OF PREVENTION,
ADVANCE DIRECTIVES)
DVT Expected findings: leg pain Management of
- Thrombophlebitis is a and tenderness thrombophlebitis
thrombus that is - unilateral area of swelling, - Bed rest and elevation
associated with warmth, and redness of the client’s extremeity
inflammation - hardened vein over the above the level of the
- Thrombophlebitis of th thrombosis heart. Encourage the
elower extremities can be - calf tenderness client to change positions
of superifical or deep Diagnostic Procedures frequently.
veins, which are the most - noninvasive procedures - - Administer intermittent
often of the femoral, droppler ultrasound or continous warm moist
saphenous, popliteral scanning. compresses.
veins. -CT - Do not massage the
- The postpartum clien tis -MRI affected limb to prevent
at greatest risk for a DVT Client education thrombus from dislodging
that can lead to a - Avoid taking aspirin or and becoming an
pulmonary embolism. ibuprofen - increasing embolus. - Measure the
bleeding tendencies client’s leg
- Use electric razor for circumferences.
shaving - Provide thigh-high
-Avoid alcohol use - inhibit antiembolism stockings
warfarin for the client at high risk
- Brush teeth gently using a for venous insufficiency.
soft toothbrush. - Administer analgesics
- Avoid rubbing or (NSAIDs)
massaging legs. - Administer
- Avoid periods of anticoagulants (Heparin
prolonged sitting or or warfarin) for DVT.
crossing legs
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A1