AP* Chemistry
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
& SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY
Chemists have used reactions to produce the materials Teflon, nylon, Dacron, Kevlar, polystyrene, and PVC
among many others!
WATER, THE COMMON SOLVENT
• Properties – Water has a high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, high
cohesive and adhesive forces. All of these properties contribute to life on this
planet!
• The H2O – the two O—H bonds are polar covalent since oxygen has a higher
electronegativity and thus the electrons are more attracted to the oxygen and
spend more time there. This creates a partial charge indicated by the Greek
lower case letter delta, δ
This unequal charge distribution makes the molecule polar. Also notice the
105° bond angle, the two unshared electron pairs are “hogs” and require
more space than shared pairs thus the usual 109.5° bond angle is squished to
about 105°
There are TWO unshared electron pairs associated with the oxygen atom that make the partial negative
charge −2δ
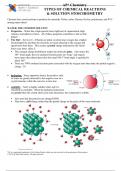
• hydration – Since opposites attract, the positive ends
of water are greatly attracted to the negative ions in a
crystal structure while the converse is also true.
• solubility – NaCl is highly soluble while AgCl is
classified as insoluble. When the hydration attractions
are greater than the crystal lattice [ion-ion] attractions, the compound is soluble.
Also note that the particles are charged IONS.
They have a full charge rather than the partial charge on the poles of the water molecule.
*AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of this product.
© 2013 by René McCormick. All rights reserved.
, Water can also dissolve nonionic substances such as alcohols and sugars among others. Alcohols and
sugars contain O—H bonds that are polar just as the O—H bond in water. This polarity makes the
molecule soluble.
Hydration in action due to
an electrostatic attraction
called a hydrogen bond.
Can also be represented
by a dashed line.
ethanol ethanol IS attracted to water
Fats do not dissolve in water since they are nonpolar.
“Like dissolves like” is a useful guideline for predicting solubility, BUT it is not an explanation!
You must address the electrostatic (“opposites attract”) aspects of solute-solvent interactions.
THE NATURE OF AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS: STRONG AND WEAK ELECTROLYTES
Remember a solution is a homogeneous mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent. Aqueous solutions
are solutions where the solvent is water.
Properties of Aqueous Solutions
• electrolytes – solutions that conduct an electric current; the more mobile & charged
particles present, the higher the concentration of ions in solution, the better the
conduction. The magnitude of the charge also matters.
• strong – completely dissociate (consult solubility rules—strong acids, strong bases and
soluble salts)
• Barium chloride is an ionic salt that completely ionizes in water, HCl is a strong acid that
completely dissociates into H+ ions and Cl− ions in water while NaOH is a strong base that
completely dissociates into Na+ ions and OH− ions water. All 3 release mobile, charged
particles that readily conduct electricity.
• COMMON Strong acids: HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4 [loses first H+ easily and exists
mainly as H+ and HSO4− ions in water], and HClO4
• COMMON Strong bases: Oxides and Hydroxides of I & II A metals [solubility issues with
the IIA’s]
• weak – do not completely dissociate; only about 1% dissociation (The weak acid, acetic
acid and the weak base ammonia are pictured right. Both are classic examples!)
Types of Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry 2
, nonelectrolytes – solutions where dissolving has occurred but the solute does not make ions and therefore
cannot conduct electricity. (Pure water, sugar, alcohols, antifreeze, and starch)
• Svante Arrhenius was the first to identify the conductive properties of solutions in the late 1890’s.
He correctly postulated that the extent to which a solution can conduct an electric current depends
directly on the number of ions present.
THE COMPOSITION OF SOLUTIONS
Chemical reactions often take place when two solutions are mixed. To perform stoichiometric calculations in
such cases two things must be known: (1) The nature of the reaction which depends on the exact substance and
whether it exists as ions or molecules in solution AND (2) the amount of chemical (number of moles) present in
the solution. Our favorite concentration unit is molarity:
moles of solute
Molarity [M ] =
Liters of solution
• Molarity – is a concentration unit of moles per liter. [NaCl] = 0.75 M means 0.75 moles of salt is
contained in 1.00 L of solution. The square brackets indicate whatever is inside is a) in solution and
b) its concentration is expressed in molarity. You may use either the square brackets or the unit M
to express units of molarity on the AP exam.
grams
M = MM
Liters of solution
Preparing Solutions of KNOWN concentration
• Weigh out the solid as accurately as possible, place in a volumetric flask, add only enough distilled
water to dissolve the solid and swirl to completely dissolve the solid THEN add a bit more water, filling
to the mark on the flask. If you dump solid into 1.00 L of water you are neglecting the space the solid
will occupy and your molar concentration will NOT be correct!
Types of Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry 3
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
& SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY
Chemists have used reactions to produce the materials Teflon, nylon, Dacron, Kevlar, polystyrene, and PVC
among many others!
WATER, THE COMMON SOLVENT
• Properties – Water has a high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, high
cohesive and adhesive forces. All of these properties contribute to life on this
planet!
• The H2O – the two O—H bonds are polar covalent since oxygen has a higher
electronegativity and thus the electrons are more attracted to the oxygen and
spend more time there. This creates a partial charge indicated by the Greek
lower case letter delta, δ
This unequal charge distribution makes the molecule polar. Also notice the
105° bond angle, the two unshared electron pairs are “hogs” and require
more space than shared pairs thus the usual 109.5° bond angle is squished to
about 105°
There are TWO unshared electron pairs associated with the oxygen atom that make the partial negative
charge −2δ
• hydration – Since opposites attract, the positive ends
of water are greatly attracted to the negative ions in a
crystal structure while the converse is also true.
• solubility – NaCl is highly soluble while AgCl is
classified as insoluble. When the hydration attractions
are greater than the crystal lattice [ion-ion] attractions, the compound is soluble.
Also note that the particles are charged IONS.
They have a full charge rather than the partial charge on the poles of the water molecule.
*AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of this product.
© 2013 by René McCormick. All rights reserved.
, Water can also dissolve nonionic substances such as alcohols and sugars among others. Alcohols and
sugars contain O—H bonds that are polar just as the O—H bond in water. This polarity makes the
molecule soluble.
Hydration in action due to
an electrostatic attraction
called a hydrogen bond.
Can also be represented
by a dashed line.
ethanol ethanol IS attracted to water
Fats do not dissolve in water since they are nonpolar.
“Like dissolves like” is a useful guideline for predicting solubility, BUT it is not an explanation!
You must address the electrostatic (“opposites attract”) aspects of solute-solvent interactions.
THE NATURE OF AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS: STRONG AND WEAK ELECTROLYTES
Remember a solution is a homogeneous mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent. Aqueous solutions
are solutions where the solvent is water.
Properties of Aqueous Solutions
• electrolytes – solutions that conduct an electric current; the more mobile & charged
particles present, the higher the concentration of ions in solution, the better the
conduction. The magnitude of the charge also matters.
• strong – completely dissociate (consult solubility rules—strong acids, strong bases and
soluble salts)
• Barium chloride is an ionic salt that completely ionizes in water, HCl is a strong acid that
completely dissociates into H+ ions and Cl− ions in water while NaOH is a strong base that
completely dissociates into Na+ ions and OH− ions water. All 3 release mobile, charged
particles that readily conduct electricity.
• COMMON Strong acids: HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4 [loses first H+ easily and exists
mainly as H+ and HSO4− ions in water], and HClO4
• COMMON Strong bases: Oxides and Hydroxides of I & II A metals [solubility issues with
the IIA’s]
• weak – do not completely dissociate; only about 1% dissociation (The weak acid, acetic
acid and the weak base ammonia are pictured right. Both are classic examples!)
Types of Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry 2
, nonelectrolytes – solutions where dissolving has occurred but the solute does not make ions and therefore
cannot conduct electricity. (Pure water, sugar, alcohols, antifreeze, and starch)
• Svante Arrhenius was the first to identify the conductive properties of solutions in the late 1890’s.
He correctly postulated that the extent to which a solution can conduct an electric current depends
directly on the number of ions present.
THE COMPOSITION OF SOLUTIONS
Chemical reactions often take place when two solutions are mixed. To perform stoichiometric calculations in
such cases two things must be known: (1) The nature of the reaction which depends on the exact substance and
whether it exists as ions or molecules in solution AND (2) the amount of chemical (number of moles) present in
the solution. Our favorite concentration unit is molarity:
moles of solute
Molarity [M ] =
Liters of solution
• Molarity – is a concentration unit of moles per liter. [NaCl] = 0.75 M means 0.75 moles of salt is
contained in 1.00 L of solution. The square brackets indicate whatever is inside is a) in solution and
b) its concentration is expressed in molarity. You may use either the square brackets or the unit M
to express units of molarity on the AP exam.
grams
M = MM
Liters of solution
Preparing Solutions of KNOWN concentration
• Weigh out the solid as accurately as possible, place in a volumetric flask, add only enough distilled
water to dissolve the solid and swirl to completely dissolve the solid THEN add a bit more water, filling
to the mark on the flask. If you dump solid into 1.00 L of water you are neglecting the space the solid
will occupy and your molar concentration will NOT be correct!
Types of Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry 3