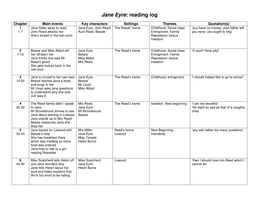
1. Key Literary Terms
● Allusion: A reference to another work, event, or person to deepen meaning (e.g.,
Biblical, historical).
● Diction: Word choice that establishes tone or conveys meaning.
● Imagery: Descriptive language that appeals to the senses.
● Symbolism: Use of symbols to represent deeper ideas (e.g., a rose = love).
● Tone: The author's attitude toward the subject (e.g., sarcastic, somber).
● Syntax: Sentence structure and its effect on the text's meaning.
2. Literary Analysis Steps
1. Read Actively: Annotate key lines, underline metaphors, and note recurring themes.
2. Identify Key Themes:
○ Common themes: Power, identity, morality, conflict, love, isolation.
3. Focus on Style: How do diction, tone, and imagery shape meaning?
4. Connect to Purpose: What is the author’s message or intent?
3. Common AP Essay Types
1. Poetry Analysis: Analyze structure, figurative language, and speaker's tone.
○ Example Prompt: How does the poet use imagery and metaphor to convey
emotion?
2. Prose Analysis: Focus on narrative voice, setting, and character development.
○ Example Prompt: How does the author use symbolism to critique society?
3. Open Question: Respond to a theme or concept using a novel or play.
○ Strategy: Choose a text you know well and tailor the argument.
4. Common Works & Themes
● Shakespeare’s Hamlet
○ Theme: Action vs. inaction, the complexity of human emotion.
○ Literary Elements: Soliloquies, imagery of decay, tragic structure.
○ Key Quote: “To be or not to be—that is the question.”
● F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby