ACTUAL Questions and CORRECT
Answers
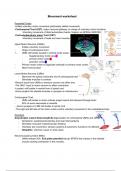
cell body (soma) - CORRECT ANSWER - Contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell
needed to sustain its life
Makes Neurotransmitters
Dendrites - CORRECT ANSWER - Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to
receive information.
myelin sheath - CORRECT ANSWER - A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the
fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the
impulse hops from one node of ranvier to the next.
Axon - CORRECT ANSWER - Carries neurotransmitters to synapse, action potentials
occur here.
Node of Ranvier and Myelin Sheath speed this process.
Nodes of Ranvier - CORRECT ANSWER - a gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve, between
adjacent Schwann cells. Speeds up propagation.
Schwann cells - CORRECT ANSWER - Type of glia in the PNS, Supporting cells of the
peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
Ogliodendrocytes - CORRECT ANSWER - Glia that Produces myelin sheath around nerve
fibers in the central nervous system (CNS)
,Synapse - CORRECT ANSWER - the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron
and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron, neurotransmission occurs here.
action potential - CORRECT ANSWER - A momentary reversal in electrical potential
across a plasma membrane that occurs when a cell has been activated by a stimulus. Driving
force of neurotransmission.
resting potential - CORRECT ANSWER - Difference in electrical charge/the state of the
neuron when not firing a neural impulse (-70 microvolts) More Na+ outside the cell, More K+
inside cell.
Depolarization (Step 2) - CORRECT ANSWER - The process during the action potential
when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive. Inputs to the
dendrites or cell bodies of neurons have an effect on the neuron.
Repolarization (Step 3) - CORRECT ANSWER - Return of the cell to resting state, caused
by reentry of potassium (K+) into the cell while sodium (Na +) exits the cell. At the peak, K+
leaves the neuron.
Hyperpolarization (Step 4) - CORRECT ANSWER - Repolarization overshoots the resting
membrane potential briefly, causing an increase in the membrane potential of a cell, relative to
the normal resting potential. New action potentials are very difficult during this time.
Glia - CORRECT ANSWER - Maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support
and protection for the neurons.
Astrocytes - CORRECT ANSWER - form the blood brain barrier and regulate the
chemical environment of the neurons
synaptic vesicles - CORRECT ANSWER - Tiny pouches or sacs in the axon terminals that
contain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
, presynaptic cell - CORRECT ANSWER - The transmitting neuron in a synapse.
postsynaptic cell - CORRECT ANSWER - The neuron, muscle, or gland cell that receives
the signal from a neuron.
synaptic cleft - CORRECT ANSWER - The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic
neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
Stimulus (Step 1) - CORRECT ANSWER - A change in an organism's surroundings that
causes the organism to initiate action potential.
Resting state (Step 5) - CORRECT ANSWER - the state in which there is a negative
electrical charge of about -70 millivolts within a neuron.
Action Potential - Unmyelinated Cell - CORRECT ANSWER - uninterrupted down the
length of the axon.
Action Potential- Myelinated Cell - CORRECT ANSWER - jumps from one Node of
Ranvier to the next because there is a concentrated number of voltage-gated ion channels in these
regions
presynaptic terminal - CORRECT ANSWER - Action potential travels here. There are
more channels open causing Ca2+ ions to flow into the terminal, which leads to docking of
synaptic vesicles.
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) - CORRECT ANSWER - Cause the next cell to
become active
inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) - CORRECT ANSWER - Prevent the next cell
from becoming active