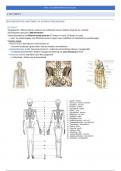
Endocrine glands & functions
Pituitary
Anterior – largest part
Hormone effect on target stimulus
for release
ACTH - stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone & cortisol
- stress
FSH -sperm production; ovarian follicles for eggs -GnRH
LH -testicular; ovulation (release of egg) -GnRH
GH - during anabolic metabolism, cartilage growth -Normal
growt/dev.
& catabolism of fat. BGL & insulin effects.
PRL -stimulates production of breast milk -estrogen,
preg/nursing
TSH -stim. Thyroid to release T3 & T4 -thyroid needs
Posterior
Hormone effect on target stimulus for
release
ADH -add h20 back into body; tells kidney to reabsorb - BP, Pain,
High osmolality
H20. Of blood.
Oxytocin -maternity: stimulate contraction & lactation of -L&D of
Newborn; infant BF.
Breast milk
Thyroid
T3 & T4 T4T3 (active thyroid hormone) w/ the help of TSH (thyroid stimulating
hormone)
Hypothalamus releases TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) THEN CAUSES the anterior
pituitary to release TSH
Thyroid stimulates & then releases T3(active thyroid hormone), T4(thyroid hormone),
Calcitonin (puts TONS of Ca IN bone)
Calcitonin TONES down the Ca in the blood put putting the Ca BACK into the bone.
Hypothyroidism: Low T3 & T4; High TSH
Hashimoto (low & slow); low dietary iodine; **Pituitary tumor!!; thyroidectomy
S/S: constipation; hypotension
Hyperthyroidism: High T3 & T4; Low TSH
#1 cause is Graves disease; Iodine excess; Levothyroxine excess
S/S: enlarged thyroid, HTN
*dietary iodine found in salt makes T3 & T4; so iodine deficiency causes hypothyroidism
TEST TIP: always focus on what the levels are for T3 & T4 first!! TSH will always be the opposite of
T3 & T4!
**TSH is just trying to SLOW down the HYPER or AMP up the HYPO
Parathyroid
PTH: parathyroid hormone Negative Feedback Loop: Ca+ HIGH PTH
SHUTS OFF
Memory trick: PTH Puts The calcium High Ca+ LOW PTH
TURNS ON
PC – Parathyroid & Calcium (9-10.5)
PTH is HIGH = Ca is HIGH How is Ca in blood? RIB
PTH is LOW = Ca is LOW R – Renals reabsorb Ca+ from urine
I – intestines (GI) absorption (help of Vit. D activation)
Hypoparathyroidism: = hypocalcemia B – Bone (into the blood)
Pituitary
Anterior – largest part
Hormone effect on target stimulus
for release
ACTH - stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone & cortisol
- stress
FSH -sperm production; ovarian follicles for eggs -GnRH
LH -testicular; ovulation (release of egg) -GnRH
GH - during anabolic metabolism, cartilage growth -Normal
growt/dev.
& catabolism of fat. BGL & insulin effects.
PRL -stimulates production of breast milk -estrogen,
preg/nursing
TSH -stim. Thyroid to release T3 & T4 -thyroid needs
Posterior
Hormone effect on target stimulus for
release
ADH -add h20 back into body; tells kidney to reabsorb - BP, Pain,
High osmolality
H20. Of blood.
Oxytocin -maternity: stimulate contraction & lactation of -L&D of
Newborn; infant BF.
Breast milk
Thyroid
T3 & T4 T4T3 (active thyroid hormone) w/ the help of TSH (thyroid stimulating
hormone)
Hypothalamus releases TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) THEN CAUSES the anterior
pituitary to release TSH
Thyroid stimulates & then releases T3(active thyroid hormone), T4(thyroid hormone),
Calcitonin (puts TONS of Ca IN bone)
Calcitonin TONES down the Ca in the blood put putting the Ca BACK into the bone.
Hypothyroidism: Low T3 & T4; High TSH
Hashimoto (low & slow); low dietary iodine; **Pituitary tumor!!; thyroidectomy
S/S: constipation; hypotension
Hyperthyroidism: High T3 & T4; Low TSH
#1 cause is Graves disease; Iodine excess; Levothyroxine excess
S/S: enlarged thyroid, HTN
*dietary iodine found in salt makes T3 & T4; so iodine deficiency causes hypothyroidism
TEST TIP: always focus on what the levels are for T3 & T4 first!! TSH will always be the opposite of
T3 & T4!
**TSH is just trying to SLOW down the HYPER or AMP up the HYPO
Parathyroid
PTH: parathyroid hormone Negative Feedback Loop: Ca+ HIGH PTH
SHUTS OFF
Memory trick: PTH Puts The calcium High Ca+ LOW PTH
TURNS ON
PC – Parathyroid & Calcium (9-10.5)
PTH is HIGH = Ca is HIGH How is Ca in blood? RIB
PTH is LOW = Ca is LOW R – Renals reabsorb Ca+ from urine
I – intestines (GI) absorption (help of Vit. D activation)
Hypoparathyroidism: = hypocalcemia B – Bone (into the blood)