FBBC Module 5 Test Study Set
Describe selective attention - Answer the focusing of conscious awareness on a
particular stimulus
Why is attention the gatekeeper of perceptions and knowledge? - Answer we can't
process information is we don't attend to it
How is attention different from arousal/vigilance? - Answer arousal or vigilance is our
overall level of alertness and affects attention
What is the difference between overt and covert attention? - Answer - overt = focus on a
stimulus or set of stimuli that coincides with sensory orientation
- covert = independent of sensory orientation
Describe the cocktail party effect - Answer our ability to filter out sensory inout from
multiple modalities and to selective attend to specific stimuli
How is shadowing task and dichotic listening connected? - Answer dichotic listening is a
type of shadowing task in which the subject wears headphones and one set of info is
presented to one ear, but another set of info is presented to another ear
What does the dichotic listening test show? - Answer performance on tasks is much
worse when trying to focus on multiple tasks or information sources at once
How does the invisible gorilla test show inattention blindness? - Answer participants
were focused elsewhere and did not notice the gorilla, a stimulus that you would think
stands out
Why is sustained attention important? - Answer 1. lets us efficiently and successfully do
things that take a long time to do
2. allows us to detect changes in the environment that might alert us something
important is happening
What is the difference between feature search and conjunction search? - Answer -
feature = search for a target in which the target pops out easily because it possesses a
unique attribute
- conjunction = search for items based on more than one feature and requires grouping
together or binding features
Which requires more effort? Feature or conjunction search? - Answer conjunction
search
Describe the feature integration theory - Answer we perform conjunction searches with
multiple cognitive feature maps
, How does the feature integration theory address the binding problem? - Answer
explains that binding of feature maps allows for individual attributes of a single stimulus
to blend into a single object, even though the individual attributes are processed by
different parts of the brain
Why are conjunction searches faster is we use a bottom up process vs. a top-down
process? - Answer - bottom up process = scan one feature at a time
- top down process = scan for all features at the same time
What is the difference between reflexive attention and voluntary attention? - Answer -
reflexive attention = bottom-up processing (controlled by inputs from lower levels of the
nervous system)
- voluntary attention = endogenous of top-down processing (controlled by higher order
cognitive processes)
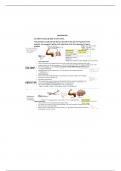
How is the superior colliculus involved in attention? - Answer guides attentional eye
movements
How is the pulvinar involved in attention? - Answer - visual processing
- orienting and shifting attention
- filters out distracting stimuli
What are the subcortical areas involved in attention? - Answer superior colliculus and
pulvinar
What are the cortical areas involved in attention? - Answer dorsal frontoparietal
(intraparietal sulcus and frontal eye field) and right temporoparietal (temporoparietal
junction)
What is the difference between the functions of the dorsal frontoparietal and right
temporoparietal? - Answer - dorsal frontoparietal = voluntary top-down control of
attention
- right temporoparietal = reflexive bottom-up shifts in attention
What happens in the intraparietal sulcus when directing attention to a particular
location? - Answer activity in the IPS enhances
What is the function of the frontal eye field? - Answer directs gaze to stimuli according
to our gaze
How is the temporoparietal junction involved in reflexive shifts in attention? - Answer
driven by characteristics of stimuli rather than cognitive control
What is hemispatial neglect and what causes it? - Answer - no attention is paid to one
side of the body or things presented to that side
Describe selective attention - Answer the focusing of conscious awareness on a
particular stimulus
Why is attention the gatekeeper of perceptions and knowledge? - Answer we can't
process information is we don't attend to it
How is attention different from arousal/vigilance? - Answer arousal or vigilance is our
overall level of alertness and affects attention
What is the difference between overt and covert attention? - Answer - overt = focus on a
stimulus or set of stimuli that coincides with sensory orientation
- covert = independent of sensory orientation
Describe the cocktail party effect - Answer our ability to filter out sensory inout from
multiple modalities and to selective attend to specific stimuli
How is shadowing task and dichotic listening connected? - Answer dichotic listening is a
type of shadowing task in which the subject wears headphones and one set of info is
presented to one ear, but another set of info is presented to another ear
What does the dichotic listening test show? - Answer performance on tasks is much
worse when trying to focus on multiple tasks or information sources at once
How does the invisible gorilla test show inattention blindness? - Answer participants
were focused elsewhere and did not notice the gorilla, a stimulus that you would think
stands out
Why is sustained attention important? - Answer 1. lets us efficiently and successfully do
things that take a long time to do
2. allows us to detect changes in the environment that might alert us something
important is happening
What is the difference between feature search and conjunction search? - Answer -
feature = search for a target in which the target pops out easily because it possesses a
unique attribute
- conjunction = search for items based on more than one feature and requires grouping
together or binding features
Which requires more effort? Feature or conjunction search? - Answer conjunction
search
Describe the feature integration theory - Answer we perform conjunction searches with
multiple cognitive feature maps
, How does the feature integration theory address the binding problem? - Answer
explains that binding of feature maps allows for individual attributes of a single stimulus
to blend into a single object, even though the individual attributes are processed by
different parts of the brain
Why are conjunction searches faster is we use a bottom up process vs. a top-down
process? - Answer - bottom up process = scan one feature at a time
- top down process = scan for all features at the same time
What is the difference between reflexive attention and voluntary attention? - Answer -
reflexive attention = bottom-up processing (controlled by inputs from lower levels of the
nervous system)
- voluntary attention = endogenous of top-down processing (controlled by higher order
cognitive processes)
How is the superior colliculus involved in attention? - Answer guides attentional eye
movements
How is the pulvinar involved in attention? - Answer - visual processing
- orienting and shifting attention
- filters out distracting stimuli
What are the subcortical areas involved in attention? - Answer superior colliculus and
pulvinar
What are the cortical areas involved in attention? - Answer dorsal frontoparietal
(intraparietal sulcus and frontal eye field) and right temporoparietal (temporoparietal
junction)
What is the difference between the functions of the dorsal frontoparietal and right
temporoparietal? - Answer - dorsal frontoparietal = voluntary top-down control of
attention
- right temporoparietal = reflexive bottom-up shifts in attention
What happens in the intraparietal sulcus when directing attention to a particular
location? - Answer activity in the IPS enhances
What is the function of the frontal eye field? - Answer directs gaze to stimuli according
to our gaze
How is the temporoparietal junction involved in reflexive shifts in attention? - Answer
driven by characteristics of stimuli rather than cognitive control
What is hemispatial neglect and what causes it? - Answer - no attention is paid to one
side of the body or things presented to that side