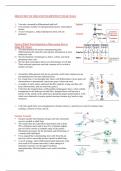
Searching
Searching data involves determining whether a value (referred to as the search key)
is present in the data and, if so, finding its location
Two popular search algorithms are the simple linear search and the faster but more
complex binary search.
Linear Search examines each element in an array one by one.
If the search key is not found: The algorithm checks every element in the array
sequentially. Once it reaches the end without finding a match, it informs the user
that the search key is not present.
If the search key is found: The algorithm continues checking elements until it finds
a match, then returns the index of that element.
// perform a linear search on the data
public static int linearSearch(int data[],int searchKey)
{
for (int index = 0; index < data.length ; index++) {
if (data[index] == searchKey)
return index;
}
return -1;
}
Big-O of Linear Search
The linear search algorithm runs in O(n) time.
Worst Case: In the worst case, every element in the array must be checked to
determine if the search item exists.
, Array Size Impact: If the array size doubles, the number of comparisons also
doubles, making the time complexity directly proportional to the array size.
Best Case: Performance can be excellent if the element is near the front of the
array, as fewer comparisons are needed.
Average Case: We aim for algorithms that perform well across all searches,
including those where the element is near the end.
Efficiency: For programs with many searches on large arrays, a more efficient
algorithm, like binary search, is preferable
Binary Search
Binary search is more efficient than linear search but requires the array to be
sorted.
1. The algorithm starts(first iteration) by checking the middle element. If it
matches the search key, the search ends.
2. If the search key is smaller than the middle element, the algorithm focuses
on the first half of the array.
3. If the search key is larger, it continues with the second half.
4. In each iteration, the middle element of the remaining portion is tested.
5. If no match is found, half of the remaining elements are eliminated with
each iteration.
6. The algorithm ends when either the element matching the search key is
found, or the remaining subarray size becomes zero.
// perform a binary search on the data
public static int binarySearch(int[] data, int key) {
int low = 0;
int high = data.length -1;
int middle = (low + high + 1) / 2;
int location = -1;