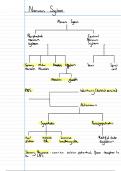
Neurons are the nerve cells that transfer information within the body. Communication by neutrons
largely consist of short distance chemical signals, or long distance electrical signals.
The brain is usually a large and complex group of neurons. A simpler and smaller group of neurons
are ganglia.
Dendrites are highly branches extensions of
the cell body. Dendrites receive information
Each neuron has a single axon, which is an
extension that transmits signals to other cells.
The axon is connected to the cell body by the
axon hillock.
The other ends of the axons are branched as
well, an transmit the information through
synapses. At most synapses, chemical
messengers (neurotransmitters) pass
information
Glia (cells) nourish neurons, insulate the
axons of neurons, and regulate the
extracellular fluid surrounding neurons.
When bundled together, the axons of neurons
form nerves.
48.1
Information processing occurs in three stages; sensory input > integration > motor output.
sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons
, The central nervous system (CNS) is a organized system, consisting of interneurons. The neurons
that carry information into and out of the CNS constitute the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
48.2
The membrane potential is the charge difference across the plasma membrane, the inside of a cell is
negatively charged relative to the outside.
For a resting neuron, the membrane potential is called the resting potential (-60 a -80 mV).
Potassium ions and sodium ions play an essential role in the formation of the resting potential. In
most neurons, the concentration potassium ions is higher inside the cell, while the concentration of
sodium ions is higher outside the cell. The gradients are maintained by the sodium-potassium pump.
These pump transports three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions. This means it
generates a net export of positive charges. Ion channels play a role in keeping the resting potential.
The equilibrium potential Eion is the magnitude of the membrane voltage equilibrium for a particular
ion.
[ ion ] outside
Eion = 62mV ( log ) = Nernst vergelijking
[ ion ] inside
48.3
When a neuron responds to a stimulus, the membrane potential changes.`
Some of the ion channels in a neuron are gated ion channels, ion channels that open or close in
response to stimuli. When a gated ion channel opens or closes, it alters the membrane’s permeability
to particular ions. This allows a rapid flow of ions, which alters the membrane potential.
Voltage gated ion channels opens or closes in response to a shift in the voltage across the plasma
membrane of the neuron.
A graded potential is a hyperpolarization (increase membrane permeability to K) or depolarization
(increase membrane permeability Na) below the threshold. An action potential occurs when a
depolarization (and so the stimulus) is strong enough to pass the threshold. Action potential;
resting state > depolarization > rising phase > falling phase > undershoot
closed some Na open most Na open most K open, Na closed, some K open
Na inactivated
The refractory period is the period when a second action potential cannot be initiated due to the
inactivated Na channels.