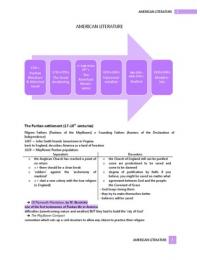
🌸
1) Cell biology
What are Eukaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells are cells which have a nucleus. Their DNA is found in
the nucleus. They divide through mitosis. A Eukaryote is an organism
which is made by eukaryotic cells.
What are Prokaryotes?
They are smaller than eukaryotic cells and do not have mitochondria or
chloroplasts. They do not have a nucleus containing their genetic
material. The DNA is a single molecule found free in the cell and can
also be in small rings of DNA called plasmids. They divide through
binary fission.
What is the structure of an animal cell?
Animal cells are Eukaryotic.
1) Cell biology 1
, The cytoplasm of animal cells is mainly water.
Most chemical reactions happen in the cytoplasm
Animal cells do not have a cell wall
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances into and out
of the cell. E.g. glucose, oxygen etc.
Mitochondria are the site of most of the cell's respiration. Here the
energy stored in glucose is is released for the cell to live. More active
cells have more mitochondria.
Unlike prokaryotic cells, the DNA of an animal cell is in the nucleus
arranged into chromosomes and the nucleus controls the activities of
the cell.
What is the structure of a plant cell?
Plant cells are also eukaryotic and are generally bigger than bacteria cells.
Like plant cells, the DNA is in chromosomes in the nucleus and they
have ribosomes for protein synthesis and mitochondria for respiration.
However they have chloroplasts not present in animal cells which
contain chlorophyll which absorbs the light necessary for
photosynthesis which produces energy for the plant. It is the
chlorophyll which makes plants green.
1) Cell biology 2
, Remember →
carbon dioxide + water → light →glucose + oxygen
Plants also have cell walls unlike animal cells made from cellulose and
provides structure.
Many plant cells unlike animal cells also have a permanent vacuole
which is filled with cell sap, the pressure in the vacuole presses the the
cytoplasm again the cell wall to keep he cell turgid.
What is the structure of a bacteria cell?
You only need to know:
cytoplasm
ribosomes
Single DNA loop (chromosome)
Plasmid DNA (small rings)
Cell membrane
1) Cell biology 3
1) Cell biology
What are Eukaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells are cells which have a nucleus. Their DNA is found in
the nucleus. They divide through mitosis. A Eukaryote is an organism
which is made by eukaryotic cells.
What are Prokaryotes?
They are smaller than eukaryotic cells and do not have mitochondria or
chloroplasts. They do not have a nucleus containing their genetic
material. The DNA is a single molecule found free in the cell and can
also be in small rings of DNA called plasmids. They divide through
binary fission.
What is the structure of an animal cell?
Animal cells are Eukaryotic.
1) Cell biology 1
, The cytoplasm of animal cells is mainly water.
Most chemical reactions happen in the cytoplasm
Animal cells do not have a cell wall
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances into and out
of the cell. E.g. glucose, oxygen etc.
Mitochondria are the site of most of the cell's respiration. Here the
energy stored in glucose is is released for the cell to live. More active
cells have more mitochondria.
Unlike prokaryotic cells, the DNA of an animal cell is in the nucleus
arranged into chromosomes and the nucleus controls the activities of
the cell.
What is the structure of a plant cell?
Plant cells are also eukaryotic and are generally bigger than bacteria cells.
Like plant cells, the DNA is in chromosomes in the nucleus and they
have ribosomes for protein synthesis and mitochondria for respiration.
However they have chloroplasts not present in animal cells which
contain chlorophyll which absorbs the light necessary for
photosynthesis which produces energy for the plant. It is the
chlorophyll which makes plants green.
1) Cell biology 2
, Remember →
carbon dioxide + water → light →glucose + oxygen
Plants also have cell walls unlike animal cells made from cellulose and
provides structure.
Many plant cells unlike animal cells also have a permanent vacuole
which is filled with cell sap, the pressure in the vacuole presses the the
cytoplasm again the cell wall to keep he cell turgid.
What is the structure of a bacteria cell?
You only need to know:
cytoplasm
ribosomes
Single DNA loop (chromosome)
Plasmid DNA (small rings)
Cell membrane
1) Cell biology 3