Answer Guidelines for Questions to Be Graded
Identifying Levels E XE RC IS E
of Measurement:
Nominal, Ordinal,
1
Interval, and Ratio
The questions are in bold followed by answers.
1. In Table 1, identify the level of measurement for the current therapy
variable. Provide a rationale for your answer.
Answer: The current therapy variable was measured at the nominal level. These drug categories were
probably developed to be exhaustive for this study and included the categories of drugs the subjects were
receiving. However, the categories are not exclusive, since patients are usually on more than one
category of these drugs to manage their health problems. The current therapies are not measured at the
ordinal level because they cannot be rank ordered, since no drug category can be considered more or less
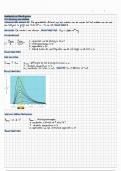
beneficial than another drug category (see Figure 1-1; Grove & Gray, 2019).
2. What is the mode for the current therapy variable in this study? Provide a
rationale for your answer.
Answer: The mode for current therapy was blocker. A total of 100 (94%) of the cardiac patients were
receiving this category of drug, which was the most common prescribed drug for this sample.
3. What statistics were conducted to describe the BMI of the cardiac patients
in this sample?
Discuss whether these analysis techniques were appropriate or inappropriate.
Answer: BMI was described with a mean and standard deviation (SD). BMI measurement resulted
in ratio-level data with continuous values and an absolute zero (Stone & Frazier, 2017). Ratio- level data
should be analyzed with parametric statistics such as the mean and SD (Grove & Gray,
2017; Knapp, 2017).
, 4. Researchers used the following item to measure registered nurses’ (RNs) income in a study: What
category identifies your current income as an RN?
a. Less than $50,000 b. $50,000 to 59,999 c. $60,000 to 69,999 d. $70,000 to 80,000 e. $80,000 or
greater
What level of measurement is this income variable? Does the income variable
follow the rules outlined in Figure 1-1? Provide a rationale for your answer.
Answer: In this example, the income variable is measured at the ordinal level. The income catego- ries are
exhaustive, ranging from less than $50,000 to greater than $80,000. The two open-ended
AG 1-1
Identifying Levels E XE RC IS E
of Measurement:
Nominal, Ordinal,
1
Interval, and Ratio
The questions are in bold followed by answers.
1. In Table 1, identify the level of measurement for the current therapy
variable. Provide a rationale for your answer.
Answer: The current therapy variable was measured at the nominal level. These drug categories were
probably developed to be exhaustive for this study and included the categories of drugs the subjects were
receiving. However, the categories are not exclusive, since patients are usually on more than one
category of these drugs to manage their health problems. The current therapies are not measured at the
ordinal level because they cannot be rank ordered, since no drug category can be considered more or less
beneficial than another drug category (see Figure 1-1; Grove & Gray, 2019).
2. What is the mode for the current therapy variable in this study? Provide a
rationale for your answer.
Answer: The mode for current therapy was blocker. A total of 100 (94%) of the cardiac patients were
receiving this category of drug, which was the most common prescribed drug for this sample.
3. What statistics were conducted to describe the BMI of the cardiac patients
in this sample?
Discuss whether these analysis techniques were appropriate or inappropriate.
Answer: BMI was described with a mean and standard deviation (SD). BMI measurement resulted
in ratio-level data with continuous values and an absolute zero (Stone & Frazier, 2017). Ratio- level data
should be analyzed with parametric statistics such as the mean and SD (Grove & Gray,
2017; Knapp, 2017).
, 4. Researchers used the following item to measure registered nurses’ (RNs) income in a study: What
category identifies your current income as an RN?
a. Less than $50,000 b. $50,000 to 59,999 c. $60,000 to 69,999 d. $70,000 to 80,000 e. $80,000 or
greater
What level of measurement is this income variable? Does the income variable
follow the rules outlined in Figure 1-1? Provide a rationale for your answer.
Answer: In this example, the income variable is measured at the ordinal level. The income catego- ries are
exhaustive, ranging from less than $50,000 to greater than $80,000. The two open-ended
AG 1-1