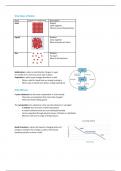
State Particle arrangement Description
Solid Regular
Close together
Vibrate around fixed position
Liquid Random
Close together
Move around each other
Gas Random
Far apart
Move in all directions
Sublimation is when a solid directly changes to a gas
It is useful as it is not wet, and is easy to place
Deposition is when a gas changes directly to a solid
- When a solid or liquid heat up, energy is going in
- When a gas or liquid cools down, energy is going out
SC2a Mixtures
A pure substance has the same composition in all its sample
- They have a composition that cannot be changed
- They have fixed melting points
The composition of a substance is the way the substance is arranged
- A mixture does not have a fixed composition
- It contains elements that are not chemically bonded
- Can be separated through physical means- filtration or distillation
- Mixtures melt over a range of temperatures
Bond formation is where the liquid is changing state and
energy is released. This energy is used to form bonds
between particles to form a solid.
,SC2b Filtration and Crystallisation
A solution is made when a solute is dissolved into the solvent
Solutes can be separated from a solution by evaporation - crystallisation
A saturated solution is when there is the highest possible concentration of a solute that can be dissolved in the
solvent at that temperature
filtration crystallisation
SC2c Paper chromatography
When a solvent moves along a strip of paper, it carries the different substances in
the mixture at different speeds, so they are separated
The paper with the separated components is the chromatogram
The solvent is called the mobile phase
The paper contains the stationary phase
The Rf value is the distance the compound has risen divided
by the distance the Rf = distance moved by the spot solvent has risen:
distance moved by the solvent
SC2d Distillation
Simple distillation:
Separates a solid from a liquid e.g.- salty water
It cannot separate a liquid from a liquid
Fractional Distillation:
Separates a liquid from a liquid
The fractioning column is used to separate the two liquids as they have different boiling points so
some liquids will evaporate quicker than others
Core Practical – Investigating inks
Use simple distillation to separate a sample of the solvent in some ink and then use paper chromatography to
separate the different substances in the ink.
, SC2e Drinking Water
Purifying sea water:
Water is separated from dissolved salts using simple distillation. Sea water is
heated so that water vapour evaporates quickly. The vapour is then cooled
and condensed leaving water without the salts.
Water for drinking:
Sedimentation is the process where rock and sediment are separated
from water to produce clean drinking water. This water is filtered
through tanks and then bacteria is killed by chlorination. This kills
microorganisms in the water.
SC3a Structure of an atom
Protons +1 charge
Nucleus
Neutrons 0
charge
Subatomic particle Relative charge Relative mass
Electrons orbit the Proton +1 1
nucleus -1 charge Neutron -1 1
Electron 0 1/1835
SC3b Atomic number and mass number
The elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of atomic number
The total amount of protons and neutrons in an atom is the mass number
SC3c Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms from the same element that have
the same atomic number but different mass number.
The relative atomic mass (Ar) is the mean mass of the isotopes.