Module 1 - An Introduction to Infancy (Historical Perspectives & Research
Methods)
Lesson 1: Introduction & Themes
Seven Themes in Child Development
1. Continuity/Discontinuity
Some researchers see development as a continuous, gradual process, akin to
a tree growing taller with each passing year pine tree: developmental
continuity
o A child’s ability to read and write may improve relatively continuously
Others see it as a discontinuous process, involving sudden dramatic changes,
such as the transition from caterpillar to cocoon to butterfly butterfly:
developmental discontinuity
o A child’s motor abilities may appear more stage like (crawling,
walking, fine-motor…)
2. Individual Differences
Individuals differ from one another even two children from within the same
family who share a lot of genetics and a lot of the same environments may
be different
What are the sources of variation?
o Genetic and epigenetic differences
o Difference in ways parents and others treat them
o Differences in children’s choices of environment
o Similar experiences affect children differently
Why study individual differences?
o Perhaps we want to know why some individuals are so resilient
o Risk factors vs. Resilience/Protective Factors
3. Nature and Nurture
Nature and Nurture are constantly interacting
Transactional Model:
o Nature & Nurture continually interact
o Influences are bidirectional e.g., child’s temperament influences
how others react
Direct vs Indirect Effects of Nature
o More direct: e.g. fearful/inhibited leads to social withdrawal
o Less direct: e.g. fearful/inhibited leads to social withdrawal which
leads to poor social understanding
4. Active Child
What role do children play in their own development?
Preferences to attend to certain things people over objects, caregiver over
others
Motivated to learn
o Little ‘experimenters’: e.g. dropping food
o Practice language in the absence of people
o Engage in pretend play
Actively seek out their own environment
o This increases significantly with age
o Friends they play with, activities they engage in, places they go, books
they read etc.
, 5. Mechanisms of Change
Brain maturation vs. experience? if brain maturation, where and when?
o E.g., frontal lobes, hippocampus
o E.g. observation/imitation, hands-on trial and error, conditioning
6. Sociocultural Context
Sociocultural context refers to the physical, social, cultural, economic, and
historical circumstances in a child’s life
7. Research and Children’s Welfare
How does child development research help children?
o Shapes social policy and the Law
o Shapes education
o Improved parenting techniques
o Improves prevention, intervention, and treatment of problems
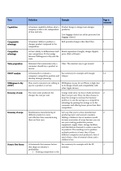
Lesson 2: Major Theories
Psychoanalytic - Largely fallen out of favour untestable
Perspective - Most influential theorists in this approach were Freud and
Erikson
- Freud made 2 important contributions importance of
early years, people can be influenced by implicit or
unconscious biases
Behaviourism and - Classical conditioning: associating a neutral stimulus with
Social Learning another stimulus that produces a reflexive response
Theory - Operant conditioning: influencing the frequency of a
behaviour by following it with reinforcers or punishment
Piaget’s Cognitive- - Famous for founding the field of Cognitive Development
Developmental - One of the broadest theories of the changes in children’s
Theory thinking
- Sensorimotor stage (1), pre-operational (2), concrete
operations (3), formal operations (4)
Information - Developmental cognitive neuroscience aims to
Processing; understand how changes in the brain change cognitive
Developmental processing and behaviour (e.g. language and memory)
Neuroscience - Developmental social neuroscience aims to understand
how changes in the brain affects emotional and social
development (e.g., adolescent depression, neurological
bases of autism)
Ethology and - Concerned with the adaptive, or survival, value of
evolutionary behaviour and its evolutionary history
developmental - Roots trace back to Darwin and his work
psychology
Vygotsky - Focuses on how culture (values, beliefs, customs, skills) is
Sociocultural Theory transmitted
- Development occurs from social interaction
Ecological Systems
Theory
Dynamic Systems
Perspective