Sunday, March 1, 2020 9:50 AM
Abbreviation Key:
freq = frequency
Week 9 Lab: Theory Concepts ampl = amplitude
Fig. = figure (of a picture in the lab manual)
w/ = with
• Simple Harmonic Motion: oscillatory behavior is the combination of many sine waves, each b/w = between
w/ their own ampl and freq.
• Natural Frequencies: frequencies at which systems execute simple harmonic motion.
○ Systems only have a few of these.
○ All other behavior can be analyzed in terms of a combination of natural frequencies.
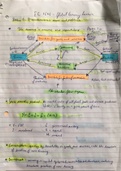
• In this lab, we will study two systems. Each have two degrees of freedom (natural
frequencies).
○ System 1: a pair of speakers, driven at a single freq (lab manual figure says they're at
slightly different freq?).
• Fig.1: function generators powering each speaker. Voltages applied to speakers
will be measured via oscilloscope. Beats monitored by adding the signals to the
oscilloscope and listening in b/w the speakers.
○ System 2: a pair of pendulums coupled by a straw.
• Fig. 2: brass bobs suspended by strings.
• Symmetric Mode: bobs oscillate in the same direction.
• Asymmetric Mode: bobs oscillate in opposite directions. Straw forces bobs to
pivot (abbreviated as h) as string remains stationary.
• Motion of System = Symmetric + Asymmetric
• If both natural frequencies of the system are excited, then "beats" appear at a freq of w1 -
w2.
○ 𝜔𝑏𝑒𝑎𝑡 = 𝜔1 - 𝜔2 (Natural frequencies of the system respectively.)
• Beats: new periodic motion at a freq lower than the natural freq. Differences b/w the natural
frequencies.
• Simple harmonic wave can be described as: 𝜓1 = 𝐴 cos 𝜔1𝑡.
○ 𝜓1 = instantaneous wave ampl
○ A = max ampl
○ w1 = angular wave frequency