Table of Contents:
Unit Topics
1.Measurements and Uncertainty 1.1 Measurements in physics
1.2 Uncertainties and Error
1.3 Vectors and scalars
2. Mechanics 2.1 Motion
2.2 Forces
2.3 Work Energy Power\
2.4 Impulse and Momentum
3. Thermal Energy 3.1 Thermal Concepts
3.2 Modeling a Gas
4. Waves 4.1 Oscillations
4.2 Travelling Waves
4.3 Wave Characteristics
4.4 Wave Behavior
4.5 Standing waves
5. Electricity 5.1 Electric fields
5.2 Heating effect of electric currents
5.3 Electric cells
5.4 Magnetic effects of electric currents
,Uncertainty:
1.2: Uncertainties and Errors
- Where unit is in the measurement tell us if the value is fractional or absolute
- Round absolute uncertainty to 1 sig fig
Propagating Uncertainty:
Addition and Subtraction
Multiplying and Dividing
,Roots and Powers
- Power or 1/m MULTIPLIED by fractional uncertainty
Mechanics:
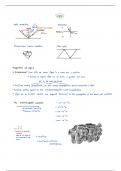
2.1: Motion
Graphs Describing Motion:
, Equations of motion for uniform acceleration:
*if acceleration is constant, the following equations can be used
V = final velocity
U = initial velocity
A = acceleration
S = displacement
T = time
Projectile Motion:
Free fall:
−2
Symbol: g Value: 9.81𝑚𝑠
*If only the force acting on a object is the force of gravity, the
object is in free fall
Rules:
−2
1. Acceleration is alway g and always points down -acceleration is 9.81𝑚𝑠 in the
y-component/ vertical direction
−1
2. If the initial velocity = 0𝑚𝑠 the object is in free fall
3. If the object is thrown upwards, its velocity at the highest point = 0
X-direction = the velocity remains the same
Y-direction the velocity changes by 9.81 - add velocities tip to tail method
Rules for 2-D Projectile motion: Movement in both horizontal and vertical direction
1. X-direction acceleration is always 0
2. You can only use kinematic equations for one direction at a time
3. Time is the only variable that changes between x and y components
Wording:
“Launched off” or “falls of flat surface” = NO initial velocity u = 0
‘Highest point in motion” or “Max height reached’ - y-velocity = 0
“Range” = total x displacement
Unit Topics
1.Measurements and Uncertainty 1.1 Measurements in physics
1.2 Uncertainties and Error
1.3 Vectors and scalars
2. Mechanics 2.1 Motion
2.2 Forces
2.3 Work Energy Power\
2.4 Impulse and Momentum
3. Thermal Energy 3.1 Thermal Concepts
3.2 Modeling a Gas
4. Waves 4.1 Oscillations
4.2 Travelling Waves
4.3 Wave Characteristics
4.4 Wave Behavior
4.5 Standing waves
5. Electricity 5.1 Electric fields
5.2 Heating effect of electric currents
5.3 Electric cells
5.4 Magnetic effects of electric currents
,Uncertainty:
1.2: Uncertainties and Errors
- Where unit is in the measurement tell us if the value is fractional or absolute
- Round absolute uncertainty to 1 sig fig
Propagating Uncertainty:
Addition and Subtraction
Multiplying and Dividing
,Roots and Powers
- Power or 1/m MULTIPLIED by fractional uncertainty
Mechanics:
2.1: Motion
Graphs Describing Motion:
, Equations of motion for uniform acceleration:
*if acceleration is constant, the following equations can be used
V = final velocity
U = initial velocity
A = acceleration
S = displacement
T = time
Projectile Motion:
Free fall:
−2
Symbol: g Value: 9.81𝑚𝑠
*If only the force acting on a object is the force of gravity, the
object is in free fall
Rules:
−2
1. Acceleration is alway g and always points down -acceleration is 9.81𝑚𝑠 in the
y-component/ vertical direction
−1
2. If the initial velocity = 0𝑚𝑠 the object is in free fall
3. If the object is thrown upwards, its velocity at the highest point = 0
X-direction = the velocity remains the same
Y-direction the velocity changes by 9.81 - add velocities tip to tail method
Rules for 2-D Projectile motion: Movement in both horizontal and vertical direction
1. X-direction acceleration is always 0
2. You can only use kinematic equations for one direction at a time
3. Time is the only variable that changes between x and y components
Wording:
“Launched off” or “falls of flat surface” = NO initial velocity u = 0
‘Highest point in motion” or “Max height reached’ - y-velocity = 0
“Range” = total x displacement