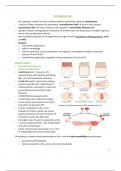
PROCESS OF PT
Direct Access GP
1. Screening technique 1. Referral from the gp
Any disease signs?
Did u sleep enough?
Have lost weight?
2. Anamnesi(basic history)
Upper/lower extremity?
How did it started?
3. Inspection(observation)
1.Total
2.Local( focus on the area where the problem is )
3.Functional ( makes the patient do an action that feels painful~)
4. ARM/PRM
Testing the range of motion through the 4 joints.
Then, muscular and diagnostic tests can be used.
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment
, Inspection:
Introduction: It’s ideal to first ask the patient from where she/he feels comfortable to start with.
Then, the patient must remove his/her clothes to have a fuller and clearer idea.During an inspection we have
to look for:
Differences in:
1. Volume muscle
2. Posture
3. Skin/texture+colour(swelling)
4. Left/right + look for asymmetries between affected and non-affected side(height of shoulders)
5. Position of joints+position of body(shifted or not?)
6. Space between the extremities and the core( if not enough then body is shifted to the side)
7. Bone deformities+deviation(kyphosis, scoliosis )
8. Straight line can be examined better from sagittal position. (appletons line)
9. Arch of the foot(saggital position)
ventral axis inspection:
Assymetries
Deformities
Volume of muscle
Shifted
Space between the extremeties and the core
Position of the body
Skin/texture of the body
Lateral position:
Arch of the foot
Appletons line
S curve
Assymetries
Volume of the muscles
Skin/texture of the body
Dorsal position:
Kyphosis,scoliosis
Assymetries
Skin and texture of the body
Shifted?
What causes impariments in movements
o Soft tissues like ligaments and muscles(Soft end feeling)
o Bones(Hard end feeling )
o Starting from active to passive ROM and compare both sides.
o Look for PAIN
Muscle length test:
Direct Access GP
1. Screening technique 1. Referral from the gp
Any disease signs?
Did u sleep enough?
Have lost weight?
2. Anamnesi(basic history)
Upper/lower extremity?
How did it started?
3. Inspection(observation)
1.Total
2.Local( focus on the area where the problem is )
3.Functional ( makes the patient do an action that feels painful~)
4. ARM/PRM
Testing the range of motion through the 4 joints.
Then, muscular and diagnostic tests can be used.
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment
, Inspection:
Introduction: It’s ideal to first ask the patient from where she/he feels comfortable to start with.
Then, the patient must remove his/her clothes to have a fuller and clearer idea.During an inspection we have
to look for:
Differences in:
1. Volume muscle
2. Posture
3. Skin/texture+colour(swelling)
4. Left/right + look for asymmetries between affected and non-affected side(height of shoulders)
5. Position of joints+position of body(shifted or not?)
6. Space between the extremities and the core( if not enough then body is shifted to the side)
7. Bone deformities+deviation(kyphosis, scoliosis )
8. Straight line can be examined better from sagittal position. (appletons line)
9. Arch of the foot(saggital position)
ventral axis inspection:
Assymetries
Deformities
Volume of muscle
Shifted
Space between the extremeties and the core
Position of the body
Skin/texture of the body
Lateral position:
Arch of the foot
Appletons line
S curve
Assymetries
Volume of the muscles
Skin/texture of the body
Dorsal position:
Kyphosis,scoliosis
Assymetries
Skin and texture of the body
Shifted?
What causes impariments in movements
o Soft tissues like ligaments and muscles(Soft end feeling)
o Bones(Hard end feeling )
o Starting from active to passive ROM and compare both sides.
o Look for PAIN
Muscle length test: