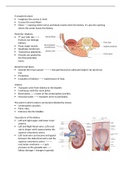
Intimate Relationships?
I. What Is an Intimate Relationship?
A. Interdependence
i. Mutual influence—affecting each others’ behavior (bidirectional)
ii. Continuity—influence extends over time
iii. Necessary for intimacy, but not sufficient
B. Emotional engagement
i. Impersonal relationships—formal, task-oriented
ii. Personal relationships—viewing partner as unique
C. Closeness
i. Close relationship—partners have strong, frequent influence over one another
across a wide range of situations
D. Sexual intimacy
i. Intimate relationship—includes sexual passion between partners that could be
expressed
, ii. Happiness not guaranteed
II. Why Are Intimate Relationships Important?
A. Evolved biological basis for human intimacy—attuned to specific intimate partners;
emotion regulation
i. Natural selection
ii. Fitness
iii. Oxytocin
B. Universal human experience
i. Pairbonds
ii. Love as a cross-cultural concept
iii. Arranged marriages
iv. Shifts in nature of and meaning of marriage in Western culture
v. Shifts in nature of conjugal relationships and childbirth patterns in Western
culture
C. Intimate relationships expand our range of emotional experiences
i. Intimate relationships are fundamentally emotional
ii. Definitions and classifications of love vary
a. Passionate love
, b. Companionate love
D. Intimate relationships affect our mental and physical health
i. Subjective well-being and relationship status
a. Selection effects
b. Protection effects
ii. Physical health and relationship status
E. Intimate relationships affect the well-being of children
i. Marital status
ii. Marital quality
F. Intimate relationships are the fabric of society—social control theory
III. What Do We Want to Know about Intimate Relationships?
A. Relationship quality
i. Why do some relationships succeed while others struggle or fail?
, CHAPTER 1: Introduction: What Do We Want to Know about
Intimate Relationships?
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. According to the textbook, the defining feature of a relationship is:
a) accepting your partner’s specific faults
b) awareness of the other
c) closeness
d) interdependence
ANS: D OBJ: Factual DIF: Easy
REF: Interdependence as the Cornerstone for Relationships
2. Which of the following is NOT a key aspect of interdependence in relationships?
a) Interdependence is bidirectional.
b) Interdependence involves continuity over time.
c) Interdependence must include intimacy.
d) Interdependence exists between two partners.
ANS: C OBJ: Factual DIF: Easy