HHIS221: HUMAN HISTOLOGY
Lesson 15 | Respiratory System
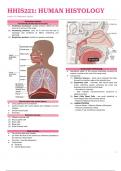
Respiratory System
Functionally divided into three parts:
(1) Ventilating mechanism: creates pressure differences that
move air in and out of the lungs.
(2) Conducting portions: carry air to and from the site of
exchange; also conditions air (filters, moistening and
warming).
(3) Respiratory portions: function for gaseous exchange.
OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM
● specialized region of the mucous membrane covering the
superior conchae at the roof of the nasal cavity.
● Components:
(1) Olfactory Neurons – Send nerve impulses that pass
through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
(2) Supporting cells – columnar, with narrow bases and
broad, cylindrical apexes containing the nuclei and
extending microvilli into the fluid layer.
– Abundant ion channels
– Help maintain microenvironment conducive to
olfactory function
(3) Stem Cells/ Basal Cells - are small, spherical, or
cone-shaped cells near the basal lamina.
Wall structure has several layers: – Replaces Olfactory Neurons (2-3mos)
● Lining epithelium from endoderm (4) LAMINA PROPRIA
● Lamina propria with mucus glands and cartilage to prevent – Serous Glands - Olfactory Glands (of Bowman)
collapse – Produce constant flow of fluid
● Smooth muscle layer – Access of new odoriferous substances
● Adventitia
Epithelial cell type:
(1) Ciliated columnar cells
(2) Mucus goblet cells
(3) Brush cells
(4) Basal cells
(5) Small Granular cells
Nasal Cavities
● The left and right nasal cavities
● Lie within the skull as two cavernous chambers separated by
the osseous nasal septum
● Conchae – bone like projections
● Components:
➔ Vestibule
➔ Internal Nasal Cavity
1
, ➔ Cuboidal cells – have various functions, including the
following:
– Secretion of surfactant lipoproteins and mucins in the
fluid layer on the epithelial surface
– Detoxification of inhaled xenobiotic compounds by
enzymes of the SER
– Secretion of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines for
local immune defense
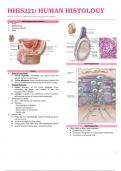
Alveoli
● small sacs which open into a bronchiole, an alveolar duct, an
atrium or an alveolar sac
● separated by thin walls of interalveolar septum specialized
for gas exchange
● with continuous capillaries forming blood-air barrier
● septum may be interrupted by pores of Kohn, to relieve or
equalize pressure and allow collateral circulation
● BLOOD-AIR BARRIER COMPONENTS:
➔ Thin cells lining the alveolus
➔ The fused basal laminae thin cells and endothelial cells
➔ The thin capillary endothelial cells
Pharynx TOPIC
● First part of the nasopharynx (1) Type 1 pneumocytes
● Contains Respiratory Epithelium ● Serves as a gas-permeable component of the blood-air
● Connects to the middle ear cavity barrier
Larynx (2) Type II pneumocytes
● Contains Hyaline Cartilage and Elastic Cartilage ● With membrane-bound lamellar / multilamellar bodies,
● Vestibular Folds secretory cells that secrete surface surfactant that
➔ Contain stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium decreases surface tension and prevents alveolar
● Vocal Folds (or cords) collapse
➔ have features important for phonation or sound (3) Alveolar Macrophages
production ● removes debris that escapes the muco-ciliary apparatus
➔ have underlying vocalis muscles that change pitch and of the conducting portion
sound of voice ● also remove blood that enter alveoli in heart failure
Epiglottis – heart failure cells
● Flattened structure projecting from the upper rim of the
larynx
● Prevents swallowed food from entering air passageways
Trachea
● Lined with typical respiratory mucosa
● Contains numerous seromucous glands producing watery
mucus
● Supported by C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
● Trachealis Muscle – Smooth Muscle and Fibroelastic Tissue
Bronchial Tree
● Left and right primary bronchi
● Secondary, tertiary and smaller bronchi
● Branches are lined by respiratory mucosa
● Branches have bands of smooth muscle and hyaline
cartilage.
Bronchioles
● Branches of the bronchial tree with diameters of 1 mm or
less.
● Lined by simple columnar or cuboidal ciliated cells.
● Terminal Bronchioles
➔ Last branches to lack alveoli
➔ Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
2
Lesson 15 | Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Functionally divided into three parts:
(1) Ventilating mechanism: creates pressure differences that
move air in and out of the lungs.
(2) Conducting portions: carry air to and from the site of
exchange; also conditions air (filters, moistening and
warming).
(3) Respiratory portions: function for gaseous exchange.
OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM
● specialized region of the mucous membrane covering the
superior conchae at the roof of the nasal cavity.
● Components:
(1) Olfactory Neurons – Send nerve impulses that pass
through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
(2) Supporting cells – columnar, with narrow bases and
broad, cylindrical apexes containing the nuclei and
extending microvilli into the fluid layer.
– Abundant ion channels
– Help maintain microenvironment conducive to
olfactory function
(3) Stem Cells/ Basal Cells - are small, spherical, or
cone-shaped cells near the basal lamina.
Wall structure has several layers: – Replaces Olfactory Neurons (2-3mos)
● Lining epithelium from endoderm (4) LAMINA PROPRIA
● Lamina propria with mucus glands and cartilage to prevent – Serous Glands - Olfactory Glands (of Bowman)
collapse – Produce constant flow of fluid
● Smooth muscle layer – Access of new odoriferous substances
● Adventitia
Epithelial cell type:
(1) Ciliated columnar cells
(2) Mucus goblet cells
(3) Brush cells
(4) Basal cells
(5) Small Granular cells
Nasal Cavities
● The left and right nasal cavities
● Lie within the skull as two cavernous chambers separated by
the osseous nasal septum
● Conchae – bone like projections
● Components:
➔ Vestibule
➔ Internal Nasal Cavity
1
, ➔ Cuboidal cells – have various functions, including the
following:
– Secretion of surfactant lipoproteins and mucins in the
fluid layer on the epithelial surface
– Detoxification of inhaled xenobiotic compounds by
enzymes of the SER
– Secretion of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines for
local immune defense
Alveoli
● small sacs which open into a bronchiole, an alveolar duct, an
atrium or an alveolar sac
● separated by thin walls of interalveolar septum specialized
for gas exchange
● with continuous capillaries forming blood-air barrier
● septum may be interrupted by pores of Kohn, to relieve or
equalize pressure and allow collateral circulation
● BLOOD-AIR BARRIER COMPONENTS:
➔ Thin cells lining the alveolus
➔ The fused basal laminae thin cells and endothelial cells
➔ The thin capillary endothelial cells
Pharynx TOPIC
● First part of the nasopharynx (1) Type 1 pneumocytes
● Contains Respiratory Epithelium ● Serves as a gas-permeable component of the blood-air
● Connects to the middle ear cavity barrier
Larynx (2) Type II pneumocytes
● Contains Hyaline Cartilage and Elastic Cartilage ● With membrane-bound lamellar / multilamellar bodies,
● Vestibular Folds secretory cells that secrete surface surfactant that
➔ Contain stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium decreases surface tension and prevents alveolar
● Vocal Folds (or cords) collapse
➔ have features important for phonation or sound (3) Alveolar Macrophages
production ● removes debris that escapes the muco-ciliary apparatus
➔ have underlying vocalis muscles that change pitch and of the conducting portion
sound of voice ● also remove blood that enter alveoli in heart failure
Epiglottis – heart failure cells
● Flattened structure projecting from the upper rim of the
larynx
● Prevents swallowed food from entering air passageways
Trachea
● Lined with typical respiratory mucosa
● Contains numerous seromucous glands producing watery
mucus
● Supported by C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
● Trachealis Muscle – Smooth Muscle and Fibroelastic Tissue
Bronchial Tree
● Left and right primary bronchi
● Secondary, tertiary and smaller bronchi
● Branches are lined by respiratory mucosa
● Branches have bands of smooth muscle and hyaline
cartilage.
Bronchioles
● Branches of the bronchial tree with diameters of 1 mm or
less.
● Lined by simple columnar or cuboidal ciliated cells.
● Terminal Bronchioles
➔ Last branches to lack alveoli
➔ Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
2