MAREX Week 3
Chapter 3 – Researching and Selecting Foreign Markets
3.1 Growth Strategies & Marketing
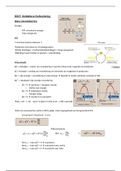
Ansoff Matrix
How can a company grow?
Choice is based on growth & export market, competitive advantage and resources available to
enter the new market.
Increasing Risk
Increasing Risk
1 3
2 4
1. Market Penetration
Focus on selling your existing products or services in your existing/home market(s)
Goal is to gain a higher market share and achieve maximum return in the home market
2. Market Development
Selling your existing products into new markets
Products may need to be attuned based on specific customer needs
3. Product Development
Creating new products for the existing customer base
This is done via R&D, by assessing customer needs and brand extension
4. Diversification Strategy
Entering a new market with a totally new product.
There are 3 diversification strategies:
a. Concentric Diversification
A company acquires or develops new products or services
Products/services are closely related to the core business
b. Horizontal Diversification
New products or services that are (unrelated) technologically or commercially but
that may appeal to current customers
Increases the firm's dependence on certain market segments
c. Conglomerate diversification
, MAREX Week 3
Adding new products/services that are significantly different from the
organization's present products/services
Expansion to unrelated areas of current business
Growth Opportunities
1. Backward vertical integration
A company integrates its operations with supply side of the business
The company gains control over the raw material suppliers by integrating them with their
ongoing business
2. Forward vertical integration
Business activities are expanded to include control of the direct distribution/supply of a
company's products
Company moves down the supply chain
e.g. farmer sells his crops at a local grocery store rather than to a distribution center that
controls grocery store placement
3. Horizontal integration
Acquisition/expansion of a business at the same level of the value chain
3.2/3.3 Growth Strategies & Segmentation, Target Groups & Positioning
Generally 3 types of marketing:
1. Mass marketing
Segment marketing (lots of competition)
e.g. products in the supermarket
2. Niche Marketing
Sub-segment marketing (little competition)
e.g. special audio installation SONOS
3. Micro Marketing
Tailor made marketing (no competition)
e.g. architect designs a house for a customer
Chapter 3 – Researching and Selecting Foreign Markets
3.1 Growth Strategies & Marketing
Ansoff Matrix
How can a company grow?
Choice is based on growth & export market, competitive advantage and resources available to
enter the new market.
Increasing Risk
Increasing Risk
1 3
2 4
1. Market Penetration
Focus on selling your existing products or services in your existing/home market(s)
Goal is to gain a higher market share and achieve maximum return in the home market
2. Market Development
Selling your existing products into new markets
Products may need to be attuned based on specific customer needs
3. Product Development
Creating new products for the existing customer base
This is done via R&D, by assessing customer needs and brand extension
4. Diversification Strategy
Entering a new market with a totally new product.
There are 3 diversification strategies:
a. Concentric Diversification
A company acquires or develops new products or services
Products/services are closely related to the core business
b. Horizontal Diversification
New products or services that are (unrelated) technologically or commercially but
that may appeal to current customers
Increases the firm's dependence on certain market segments
c. Conglomerate diversification
, MAREX Week 3
Adding new products/services that are significantly different from the
organization's present products/services
Expansion to unrelated areas of current business
Growth Opportunities
1. Backward vertical integration
A company integrates its operations with supply side of the business
The company gains control over the raw material suppliers by integrating them with their
ongoing business
2. Forward vertical integration
Business activities are expanded to include control of the direct distribution/supply of a
company's products
Company moves down the supply chain
e.g. farmer sells his crops at a local grocery store rather than to a distribution center that
controls grocery store placement
3. Horizontal integration
Acquisition/expansion of a business at the same level of the value chain
3.2/3.3 Growth Strategies & Segmentation, Target Groups & Positioning
Generally 3 types of marketing:
1. Mass marketing
Segment marketing (lots of competition)
e.g. products in the supermarket
2. Niche Marketing
Sub-segment marketing (little competition)
e.g. special audio installation SONOS
3. Micro Marketing
Tailor made marketing (no competition)
e.g. architect designs a house for a customer