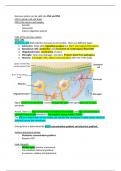
Nervous system can be split into CNS and PNS
CNS is spinal cord and brain.
PNS is the nerves and ganglia.
- Somatic
- Autonomic
- Enteric (digestive system)
Cells of the nervous system
Glial cells
Accessory cells that help the neurones in its function. There are different types:
1. Astrocytes- helps with regulating synapses but don’t send signals themselves.
2. Ependymal cells- production and movement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
3. Oligodendrocytes- myelination of axons.
4. Microglia- ‘brain macrophages’, microbes. Protects brain from pathogens.
5. Neurons- messenger cells, allows communication with rest of the body.
Signal comes in via dendrites, travels through the axon and signal goes out via axon
terminals.
At rest, there is a high concentration of sodium ions outside and high concentration of
potassium ions inside therefore a net negative charge inside (-70mV)
The different distribution of ions inside and outside the membrane is what causes electrical
potential across the membrane.
Driving force is determined by BOTH concentration gradient and electrical gradient.
Sodium-potassium pumps
- Maintains concentration gradient.
- Requires ATP
Leak channels
- Always open (passive movement)
- Can establish electrical gradient.
- In neurons- sodium and potassium.
CNS is spinal cord and brain.
PNS is the nerves and ganglia.
- Somatic
- Autonomic
- Enteric (digestive system)
Cells of the nervous system
Glial cells
Accessory cells that help the neurones in its function. There are different types:
1. Astrocytes- helps with regulating synapses but don’t send signals themselves.
2. Ependymal cells- production and movement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
3. Oligodendrocytes- myelination of axons.
4. Microglia- ‘brain macrophages’, microbes. Protects brain from pathogens.
5. Neurons- messenger cells, allows communication with rest of the body.
Signal comes in via dendrites, travels through the axon and signal goes out via axon
terminals.
At rest, there is a high concentration of sodium ions outside and high concentration of
potassium ions inside therefore a net negative charge inside (-70mV)
The different distribution of ions inside and outside the membrane is what causes electrical
potential across the membrane.
Driving force is determined by BOTH concentration gradient and electrical gradient.
Sodium-potassium pumps
- Maintains concentration gradient.
- Requires ATP
Leak channels
- Always open (passive movement)
- Can establish electrical gradient.
- In neurons- sodium and potassium.