their Application
C: Explore manufacturing techniques
and testing methods for an organic solid
Anonymous
BTEC Level 3 Applied Sciences
INTRODUCTION:
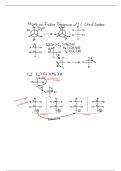
, Aspirin is a generic term for acetylsalicylic acid. This substance was
first introduced in the late 1890s, that has become a ‘’non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drug’’, non-opioid analgesic and antiplatelet drug which is
widely used for medicinal purposes. Aspirin will not react against the acetic
conditions of the stomach, yet it is hydrolysed in the intestines as it will
react on alkaline conditions to create ethanoate ions and salicylate.
Aim: In this practical, an Aspirin will be made by using laboratory
techniques and will identify the percentage yield and purity of the
substance.
Requirements:
Part 1
salicylic acid – 6.02g
100 cm3conical flask
10 cm3 measuring cylinder
ethanoic anhydride - 10cm3
concentrated sulfuric acid in a dropping bottle
400 cm3 beaker
Tripod, gauze and Bunsen burner
Thermometer (-10°C to 110 °C)
250 cm3 beaker
Reduced pressure filtration apparatus
Filter paper
Glass stirring rod
Deionised or distilled water in a wash bottle
Spatula
pipette
Part 2
25 cm3 measuring cylinder
Boiling tube
ethanol
Thermometer (-10 °C to 110 °C)
Deionised or distilled water in a wash bottle
250 cm3 beaker
100 cm3 conical flask
Glass stirring rod
A kettle