FLG 211 Copyright Micaela de Jager
Unit 2 – Muscle Physiology
UNIT 2 – LECTURE 1: SKELETAL MUSCLE
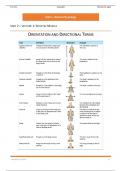
ORIENTATION AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS
MICAELA DE JAGER 31
,FLG 211 Copyright Micaela de Jager
ANATOMICAL PLANES
Median or midsagittal:
- Single imaginary vertical line
- Long axis of the body
- Divides body into 2 identical right and left halves
Sagittal plane:
- Divides body into left and right halves
- Any vertical line at any place of the body
Coronal or frontal plane
- Any vertical line
- Perpendicular to the median or midsagittal plane
- Divides body into a front (anterior) and back (posterior) half
Transverse or horizontal plane
- Any plane perpendicular to both the median and coronal planes
- Divides body into an upper (superior) and lower (inferior) half
Oblique plane
- Movement – around oblique axis
- Any movement that cannot be explained with the sagittal, frontal
or horizontal plane is normally in oblique plane
Eg.
o Golf swing
o Tennis serve
MICAELA DE JAGER 32
, FLG 211 Copyright Micaela de Jager
ANATOMICAL POSITION
• Body is in erect position
• Head, eyes and toes facing forward
• Upper limbs at side of body
• Palms facing forward (anterior)
• Thumbs facing outward (lateral)
WHAT CAUSES MOVEMENT?
STIMULUS ENERGY LEVER
➢ Get message from the brain ➢ food which is transformed into ➢ joint
that you need to move. “usable” energy known as ➢ muscles
➢ nerves – nervous system ➢ tendons
➢ motor – action ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ➢ bones (skeletal system)
➢ sensory – sensing
➢ used to sustain movement
MAIN FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES
• Contraction
• Support
• Generate motion
• Generate force Striations
• Generate heat
Types of muscles Intercalated discs
No striations
MICAELA DE JAGER 33
Unit 2 – Muscle Physiology
UNIT 2 – LECTURE 1: SKELETAL MUSCLE
ORIENTATION AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS
MICAELA DE JAGER 31
,FLG 211 Copyright Micaela de Jager
ANATOMICAL PLANES
Median or midsagittal:
- Single imaginary vertical line
- Long axis of the body
- Divides body into 2 identical right and left halves
Sagittal plane:
- Divides body into left and right halves
- Any vertical line at any place of the body
Coronal or frontal plane
- Any vertical line
- Perpendicular to the median or midsagittal plane
- Divides body into a front (anterior) and back (posterior) half
Transverse or horizontal plane
- Any plane perpendicular to both the median and coronal planes
- Divides body into an upper (superior) and lower (inferior) half
Oblique plane
- Movement – around oblique axis
- Any movement that cannot be explained with the sagittal, frontal
or horizontal plane is normally in oblique plane
Eg.
o Golf swing
o Tennis serve
MICAELA DE JAGER 32
, FLG 211 Copyright Micaela de Jager
ANATOMICAL POSITION
• Body is in erect position
• Head, eyes and toes facing forward
• Upper limbs at side of body
• Palms facing forward (anterior)
• Thumbs facing outward (lateral)
WHAT CAUSES MOVEMENT?
STIMULUS ENERGY LEVER
➢ Get message from the brain ➢ food which is transformed into ➢ joint
that you need to move. “usable” energy known as ➢ muscles
➢ nerves – nervous system ➢ tendons
➢ motor – action ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ➢ bones (skeletal system)
➢ sensory – sensing
➢ used to sustain movement
MAIN FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES
• Contraction
• Support
• Generate motion
• Generate force Striations
• Generate heat
Types of muscles Intercalated discs
No striations
MICAELA DE JAGER 33